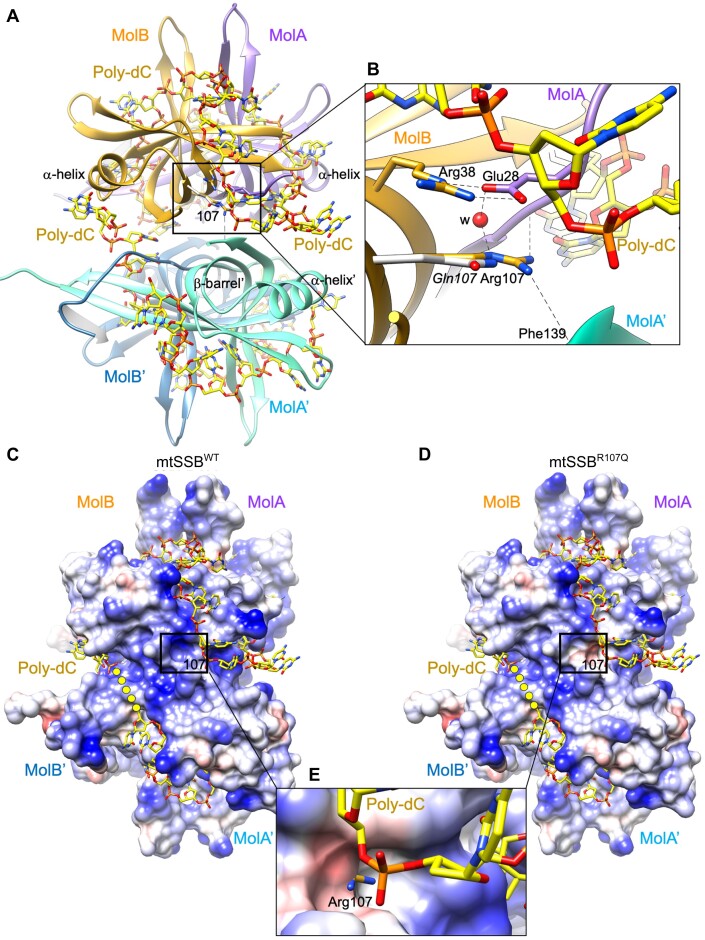
Figure 6.
Analysis of the effects of the R107Q mutation on the structure of mtSSB. (A) Two molecules MolA (colored in violet) and MolB (in gold) are related by a two-fold axis, forming a dimer that is related by crystallographic symmetry to a second dimer (MolB’ and MolA’, in light and dark blue, respectively), generating the physiological tetramer. By superposing the SSB protein from E. coli bound to a poly-dC 35-mer (PDB ID: 1EYG) onto the mtSSB structure (6RUP), the ssDNA fragments originally traced in EcSSB locate on the mitochondrial mtSSB tetramer, covering the region of Arg107 residue (framed). The β-barrel is indicated for MolA’, and so is the α-helix for monomer MolA, MolB and MolA’. (B) Close-up view showing the interaction of Arg107 with surrounding residues, which include Arg38 from the same molecule (by van der Waals interactions between the methylene groups of respective side chains), Glu27 from MolA, and Phe139 amide from MolA’. A water molecule (‘w’ red sphere) stabilizes the interactions. The modeled R107Q mutation (14) shows that the Gln shorter side chain changes the charge of the surface, from a positive charge to a polar side chain. Side chains of residues are represented in the color of the own molecule, the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in blue and red, respectively. (C, D) The electrostatic potential represented on a Conolly surface (electronegative and positive potentials shown in red and blue, respectively) of the mtSSBWT and modeled mtSSBR107Q structures, respectively. The surface at position 107 is framed, and the connection between DNA fragments is represented as yellow dots. Note that the positive electrostatic potential in the WT changes to negative potential in the mutant, near the ssDNA. (E) Close-up view of the R107Q electrostatic surface superposed to the WT structure. The surface around shorter Gln107 is electronegative and extends below the positively charged side chain of Arg107, whose charged tip protrudes.