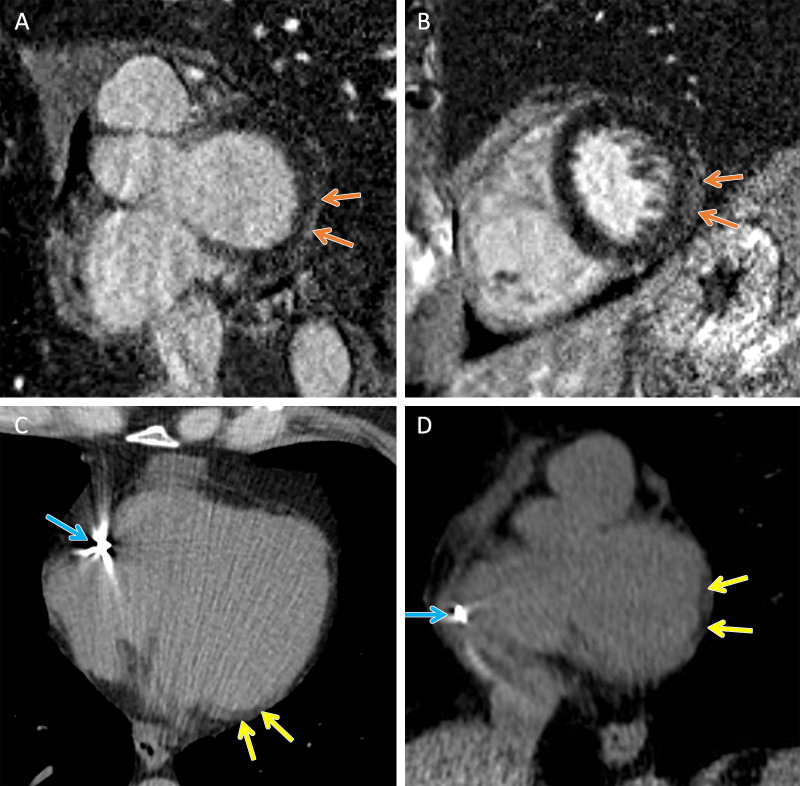
Figure 2:
TMEM43 arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Cardiac CT and MR images in a female patient between 50 and 59 years of age (exact age not provided due to potential reidentification risk) with a TMEM43 variant of unknown significance (p.Glu142Gly) with premature ventricular beats at Holter monitoring. (A, B) Short-axis late gadolinium enhancement images at the (A) base and (B) midventricle demonstrate subepicardial late gadolinium enhancement involving the basal to mid inferolateral wall (orange arrows). (C) Axial and (D) short-axis noncontrast cardiac CT images demonstrate subepicardial fat along the lateral basal left ventricular wall (yellow arrows) and right ventricular implantable cardioverter defibrillator lead (blue arrows).