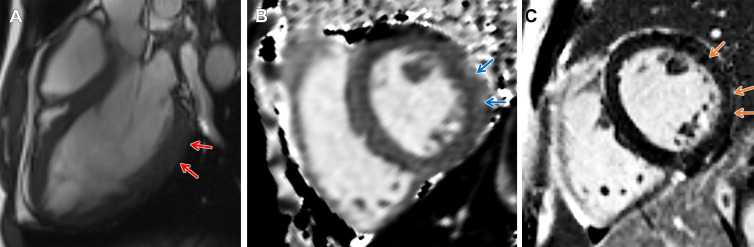
Figure 4:
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy with TMEM43 pathogenic variant (p.Ser358Leu). Short-axis 3-T MR images in a male patient between 18 and 19 years of age (exact age not provided due to potential reidentification risk) with palpitations and premature ventricular beats at Holter monitoring. He had a family history of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy in his grandfather, father, and brother. (A) Three-chamber steady-state free precession MR image demonstrates subepicardial chemical shift artifact along the basal to mid left ventricular inferolateral wall (red arrows). (B) Native T1 map demonstrates regional high T1 values at the subepicardial midventricular inferolateral wall (blue arrows). (C) There is subepicardial late gadolinium enhancement involving the midventricular anterior wall, anterolateral wall, and inferolateral wall (orange arrows).