Fig. 2 |. Genetically encoded indicators used to measure neurotransmitters and neuromodulators.
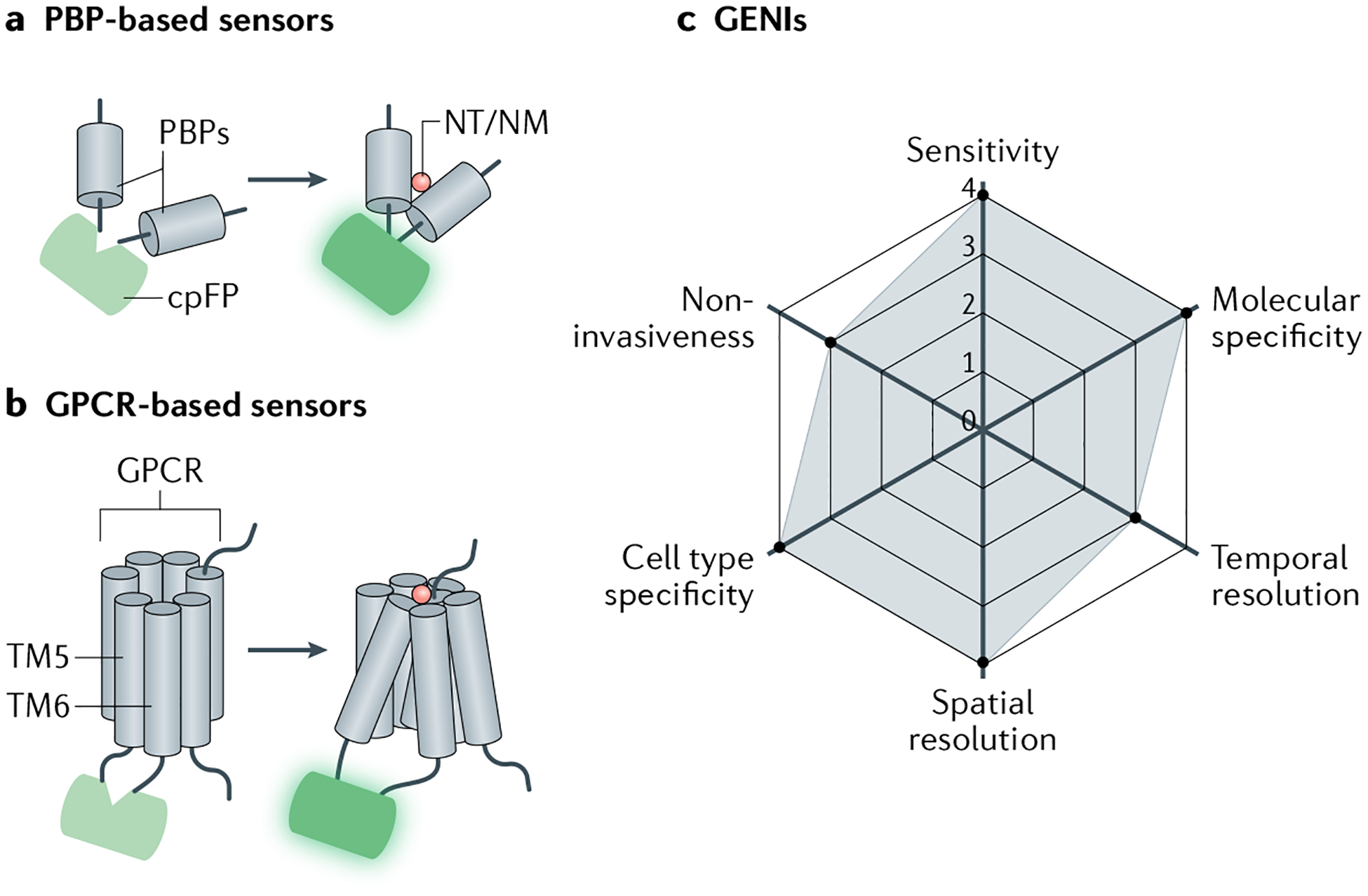
a | Periplasmic-binding protein (PBP)-based genetically encoded neurotransmitter or neuromodulator (NT/NM) indicators (GENIs) contain a circularly permuted fluorescent protein (cpFP) moiety. Following NT or NM binding, conformational changes of PBP will change fluorescence of cpFP. b | G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-based GENIs. Similar to PBP-based sensors, cpFP moiety is inserted into the intracellular loop of GPCR between transmembrane domains 5 and 6 (TM5 and TM6). Following NT or NM binding, conformational changes of GPCR induce changes in fluorescence of cpFP. c | Radar chart summarizing performance index of GENIs in arbitrary units, as in Fig. 1.
