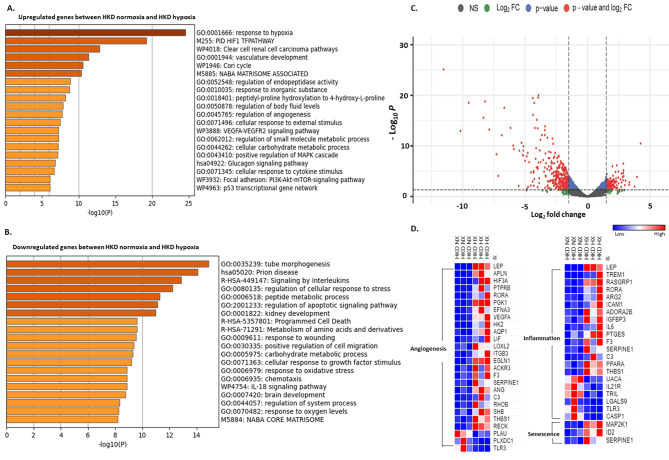
Fig. 7.
Normoxic HKD vs. hypoxic HKD MSCs. Gene ontology (GO) analysis of hallmark and biological process of upregulated (A) and downregulated (B) gene sets respectively with significant changes between normoxic HKD and hypoxic HKD MSCs. Volcano plot of dysregulated genes between normoxic HKD and hypoxic HKD MSCs (C). The vertical axis (y-axis) corresponds to the -log (p-value) and the horizontal axis (x-axis) displays the log-fold change value. Genes with higher and lower levels between normoxic HKD and hypoxic HKD MSCs are shown with red and blue dots, respectively, while non-significant genes are shown as grey dots. Specifically, red dots represent significance with the p-value and log2 FC, blue dots represent significance with p-values only, and the green dots represent significance with the log2 FC values. Heat map of genes with significant changes in normoxia HKD vs. hypoxic HKD MSCs for angiogenesis, inflammation, and senescence (D)
HC: Healthy control; HTN: Hypertension; HKD: Hypertensive Kidney disease; MSC: Mesenchymal Stem Cells; IFN- γ: Interferon gamma; IL-1α: Interleukin-1 alpha; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-8: Interleukin 8; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte Growth Factor; SA-β-gal: Senescence-associated beta-galactosidase