Fig. 4.
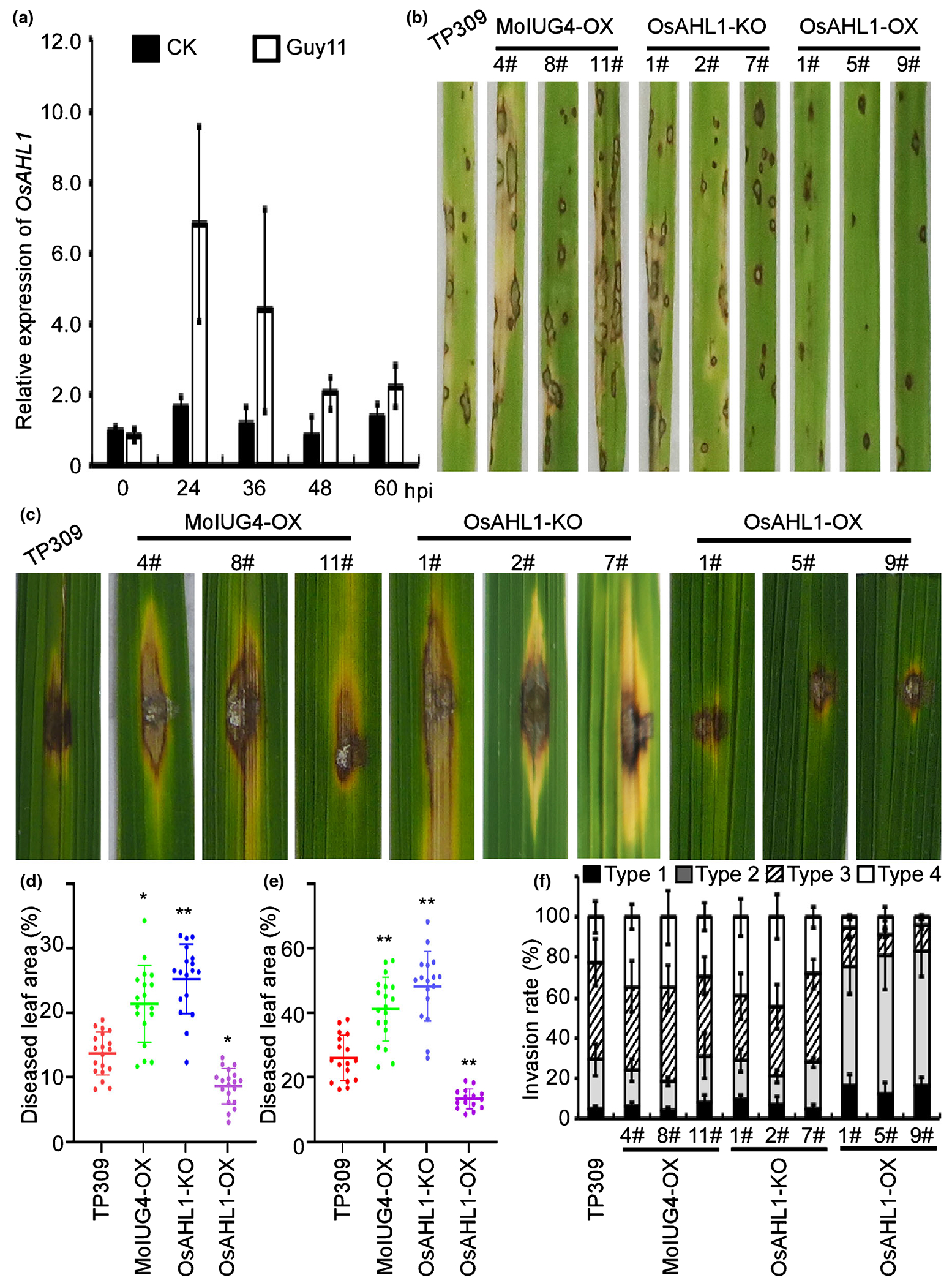
Oryza sativa OsAHL1 positively regulates rice resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. (a) Expression of OsAHL1 at different stages of M. oryzae infection was determined by quantitative real-time (qRT)-PCR. Two-week-old leaves from cv. CO-39 were inoculated with M. oryzae. CK represents H2O control. Error bars represent SD. (b) Blast resistance of OsAHL1 CRISPR knockout mutant (OsAHL1KO), MoIUG4 overexpression mutant (MoIug4-OX) and OsAHL1 overexpression mutant (OsAHL1-OX) plants using spraying inoculation. (c) Leaves of 4-wk-old plants were inoculated using the punch method. Photos were taken at 6 d post-inoculation (dpi). (d) The diseased leaf area infected with Guy11 through spraying inoculation was assessed by ImageJ. Lesions were photographed and measured or scored at 7 dpi. Error bars represent SD. Student’s t-test: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (e) Diseased leaf areas by punch injection were assessed by ImageJ. Lesions were photographed and measured or scored at 6 dpi. Error bars represent SD. Student’s t-test: **, P < 0.01. (f) Excised rice sheaths from 3-wk-old rice seedlings were inoculated with conidial suspension (1 × 105 spores ml−1). Detailed observation and statistics for infectious growth in rice sheath cells at 36 h post-inoculation (hpi). Appressorium penetration sites (n = 100) were observed and invasive hyphae (IH) were rated from type 1 to 4. The experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent SD.
