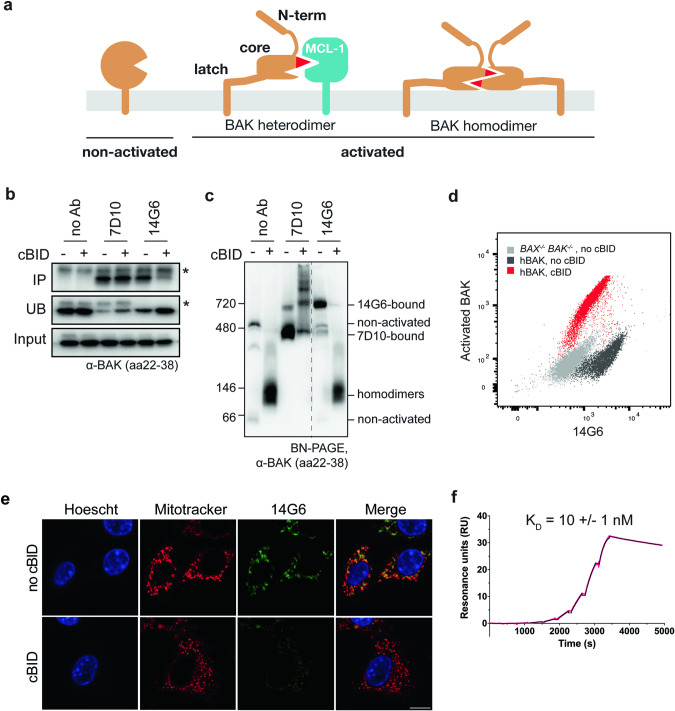
Fig. 1. The 14G6 antibody binds specifically to non-activated BAK.
a Diagram of three BAK conformations present in cells. Non-activated BAK is anchored in the mitochondrial outer membrane via a C-terminal transmembrane domain (α9) [53], with the remaining 8 helices forming a globular protein with hydrophobic surface groove [44]. Upon activation, the N-terminus (α1) and latch (α6-α8) separate from the core (α2–α5). Activated BAK can be sequestered by prosurvival proteins (e.g. MCL1) or can pair up as homodimers capable of pore formation. b 14G6 immunoprecipitates BAK only prior to its activation by cBID. Membrane fractions from bak−/−bax−/− MEFs expressing hBAK were incubated with or without cBID (30 °C, 30 min). Samples were then solubilized in 1% digitonin and immunoprecipitated with no antibody or with 7D10 or 14G6. The immunoprecipitated (IP), unbound (UB) and input fractions were immunoblotted for BAK (clone aa23-38). Data are representative of two independent experiments. c 14G6 gel-shifts BAK only prior to its activation by cBID. Membrane fractions treated as in (b) were moved to ice and incubated with the indicated antibodies for 30 min, solubilized with 1% digitonin and run on blue-native PAGE (BN-PAGE) before immunoblotting for BAK (clone aa23–38). On BN-PAGE, non-activated BAK (lane 1) tends to run as a monomer (~66 kD) or in a complex with VDAC2 (~480 kD) [55]. Note that 7D10 gel-shifts BAK both before and after its activation, and when bound to BAK homodimers can generate a ladder indicating homodimers are in clusters. Note also that 14G6-bound BAK routinely runs at a significantly higher molecular weight (~720 kD) than 7D10 bound to non-activated BAK (~480 kD). Dashed line indicates deletion of lanes from the gel. Data are representative of two independent experiments. d 14G6 specificity for non-activated BAK on flow cytometry. Membrane fractions treated as in (b) were stained with 14G6 and with the G317-2 antibody to activated BAK prior to analysis by flow cytometry. (Also see Fig. S1a). Data are representative of two independent experiments. e 14G6 specificity for non-activated BAK on immunocytochemistry. Membrane fractions treated as in (b) were stained with 14G6-AF488, Mitotracker Deep Red and Hoescht prior to analysis by immunocytochemistry. Bar, 5 μm. Data are representative of two independent experiments. f 14G6 binds to BAK with a KD of 10 nM as determined by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Kinetic parameters were determined by capturing 14G6 on a Protein A chip and injecting a threefold dilution series of BAK in a single-cycle kinetic method (0, 0.45, 1.4, 4, 12, 37, 111, 333, 1000 nM). KD is the average of three independent experiments ± standard deviation. Sensorgram shown is representative of these experiments. Raw data are shown in pink, fitted curve in black.