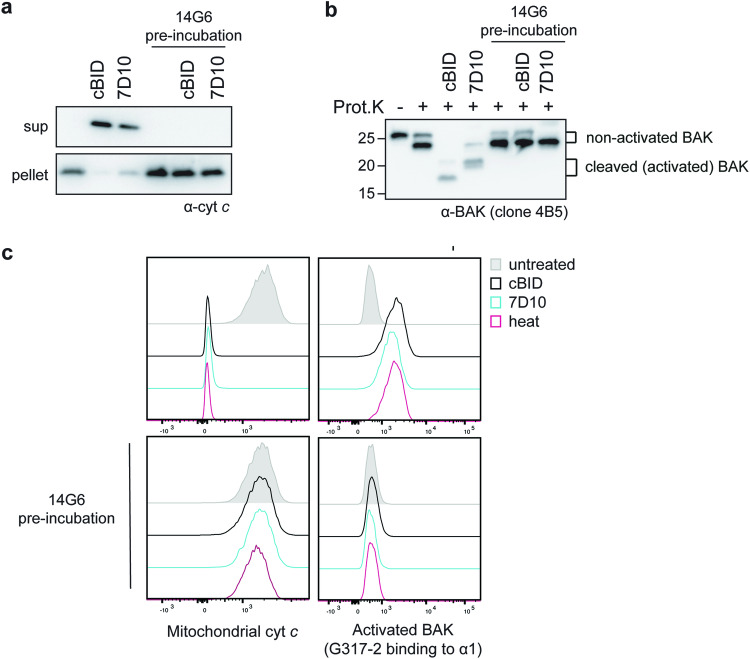
Fig. 2. 14G6 prevents BAK activation and cytochrome c release.
a 14G6 blocks cytochrome c release triggered by cBID or 7D10. bak−/−bax−/− MEFs expressing hBAK were permeabilized and incubated with or without 14G6 (on ice, 10 min) prior to incubation with or without cBID or 7D10 (30 °C, 30 min). Samples were then centrifuged and supernatant and pellet fractions immunoblotted for cytochrome c. Data are representative of two independent experiments. b 14G6 inhibits unfolding of BAK as shown by limited proteolysis. The pelleted mitochondrial fractions from (a) were treated with proteinase K and immunoblotted with antibody to the BAK BH3 domain (clone 4B5). After proteinase K, non-activated BAK runs as an ~23 kD fragment (lane 2), while cBID-activated BAK is seen as a ~16 kD fragment (lane 3) due to cleavage in the α1–α2 loop, and 7D10-activated BAK runs as a slightly larger fragment as 7D10 masks one of the cleavage sites [19]. Data is representative of two independent experiments. c 14G6 blocks BAK activation and cytochrome c release triggered by three distinct stimuli. bak−/−bax−/− MEFs expressing hBAK were permeabilized and incubated with or without 14G6 prior to incubation with or without cBID or 7D10 as indicated. Additional aliquots were also incubated at 43 °C (heat) to activate BAK. Cells were fixed and stained for cytochrome c or for activated BAK (clone G317-2) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.