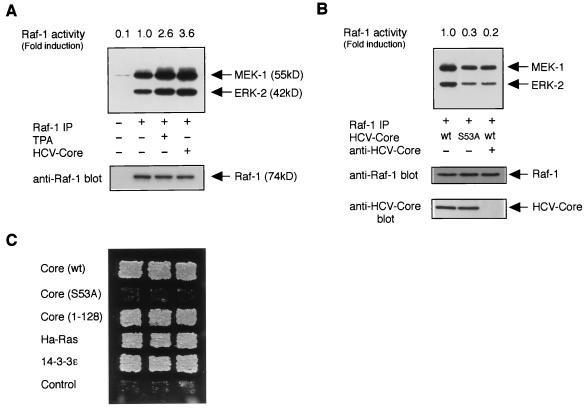
FIG. 3.
HCV core protein activates the kinase Raf-1. (A) An in vitro-coupled kinase assay for Raf-1 was performed with extracts from HepG2 (untreated or treated with TPA) or HepΔNCTH [HCV core (+)] cells. Phosphorylated MEK-1 and ERK-2 are indicated (top panel, arrows). The levels of immunoprecipitated Raf-1 are shown (bottom panel, arrows). Relative Raf-1 activities (fold induction; the 32P incorporation into ERK-2) shown are the means for duplicate determination and are representative of three experiments. (B) Extracts from HepΔNCTH cells expressing wild-type HCV core protein (wt) and HepΔNCTH (S53A) cells expressing the S53A mutant of HCV core protein (S53A) were subjected to an in vitro-coupled kinase assay. (Top panel) In the right lane, HCV core protein in cell extract was preabsorbed by using anti-HCV core antibody. (Bottom panel) The presence of HCV core protein in precleared lysates was verified by Western blot analysis. (C) Mammalian Raf-1 activation assay in yeast. Yeast strain SY1984RP cells were transformed with plasmids expressing wild-type [Core (wt)] or S53A mutant [Core (S53A)] of full-length HCV core protein, truncated HCV core protein (Core 1-128), Ha-Ras, 14-3-3ɛ, and pVT102-L empty vector (Control). Activation of Raf-1 was monitored by growth on a histidine-deficient SC plate with 3 days of incubation at 30°C.