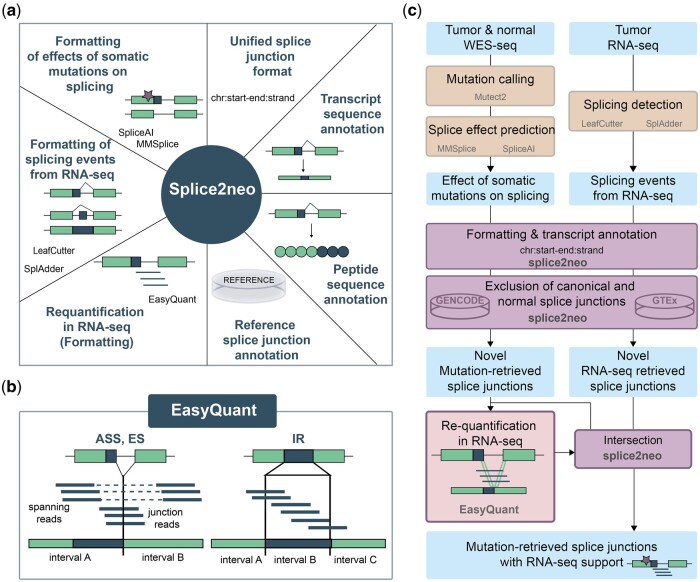
Figure 1.
The tools splice2neo and EasyQuant provide diverse functions for identifying and analyzing of splice junctions as a source of neoantigen candidates. (a) Overview of functionalities implemented in the splice2neo R package. Splice2neo formats the output of several splicing tools into a unified junction format “chr: start-end: strand,” can exclude canonical or normal splice junctions (e.g. from GENCODE or GTEx) and annotates altered transcript and peptide sequences. (b) EasyQuant implements a targeted mapping approach to quantify RNA-seq reads that support a splice junction or retained intron. (c) Workflow to detect candidate splice junctions. The effect of somatic mutations on splicing was predicted with SpliceAI and MMSplice, and expressed splicing events were detected with LeafCutter and SplAdder for a given tumor sample, followed by formatting with splice2neo into the unified splice junction format. Novel mutation and RNA-seq retrieved splice junctions were intersected to identify mutation-retrieved splice junctions with RNA-seq support as candidates. To expand the number of candidates, novel mutation-derived were requantified in tumor RNA-seq with EasyQuant in a targeted manner.