Figure 10.
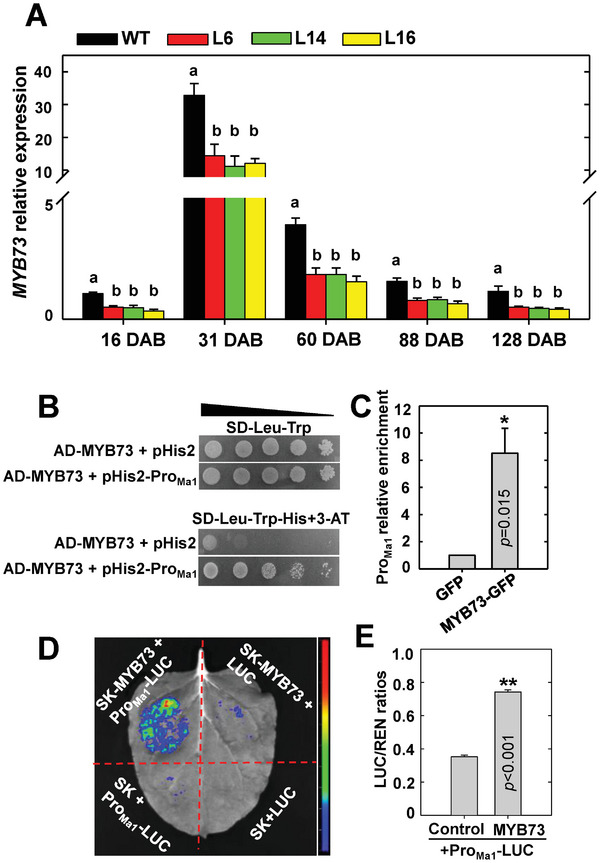
MYB73 binds to the Ma1 promoter in regulating its expression. A) Expression levels of MYB73 in fruits of WT and cMa1‐OE lines (L6, L14, L16) over five developmental stages as described in Figure 1. Quantitative RT‐PCR was performed using gene‐specific primers (Table S3, Supporting Information), with actin as the internal reference gene. Data are mean ± SE of five biological replicates, with six fruits pooled from two trees per replicate. Different letters (a, b) indicate significant differences between groups using Tukey's HSD test at p < 0.05 after ANOVA. B) Y1H assays on the binding of MYB73 protein to the Ma1 promoter sequence, with empty vector (pHis2) as a negative control. The positive clones were cultured on SD‐Leu‐Trp‐His in the presence of 3‐AT (50 mm) over a range of yeast concentrations (100 to 10−4) (represented by the triangle). The experiment was repeated three times. C) ChIP‐PCR confirmation of the binding of MYB73 protein to the Ma1 promoter. The MYB73–DNA complex was co‐immunoprecipitated from MYB73‐GFP transgenic apple calli using a GFP antibody, with empty GFP vector transgenic apple calli as a negative control. Data are mean ± SE of three biological replicates, with calli grown in one petri dish as a replicate. ** Represents significant differences using Student's t‐test at p < 0.01. D) Representative image of enhanced LUC activity in N. benthamiana leaves as a result of MYB73 binding to the Ma1 promoter. E) Promoter activity expressed as the LUC/REN ratio for the Ma1 promoter‐LUC reporter in response to overexpression of MYB73 shown in (D). Data are mean ± SE of three biological replicates, with three leaves per replicate. ** Represents significant differences using Student's t‐test at p < 0.01.
