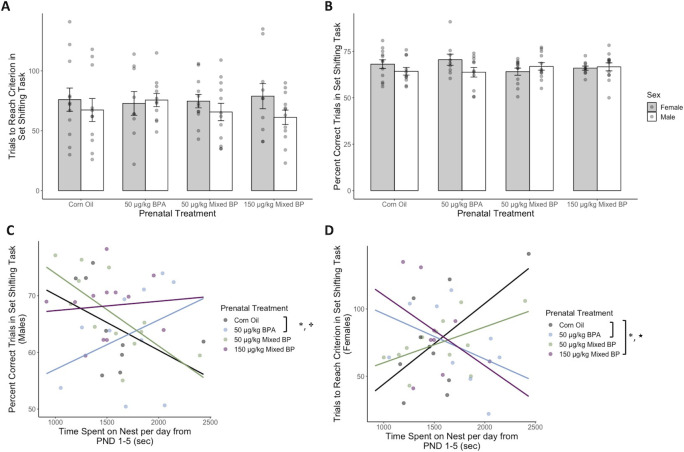
Fig 3. Prenatal bisphenol exposure was associated with reduced attentional set shifting performance after accounting for postnatal nest attendance from PND 1–5 for male and female offspring.
No main effects of prenatal treatment were found for (A) trials to reach criterion or (B) percent correct trials in the attentional set shifting response task. A marginal interaction between prenatal treatment and postnatal nest attendance was found for (C) percent correct trials for male offspring. A significant interaction between prenatal treatment and postnatal nest attendance was found for (D) trials to reach criterion for female offspring. After accounting for postnatal nest attendance, the 50 μg/kg BPA (male and female offspring) and 150 μg/kg Mixed BP (female offspring only) exposure groups showed reduced attentional set shifting performance compared to the Corn Oil group. Bar plots are displayed with mean +/- SEM with individual datapoints. Scatterplots are displayed with linear regression lines for each prenatal treatment group. * p < 0.05 main effect of prenatal treatment; ★ p < 0.05 interaction between prenatal treatment and postnatal maternal care; ✤ p < 0.10 interaction between prenatal treatment and postnatal maternal care.