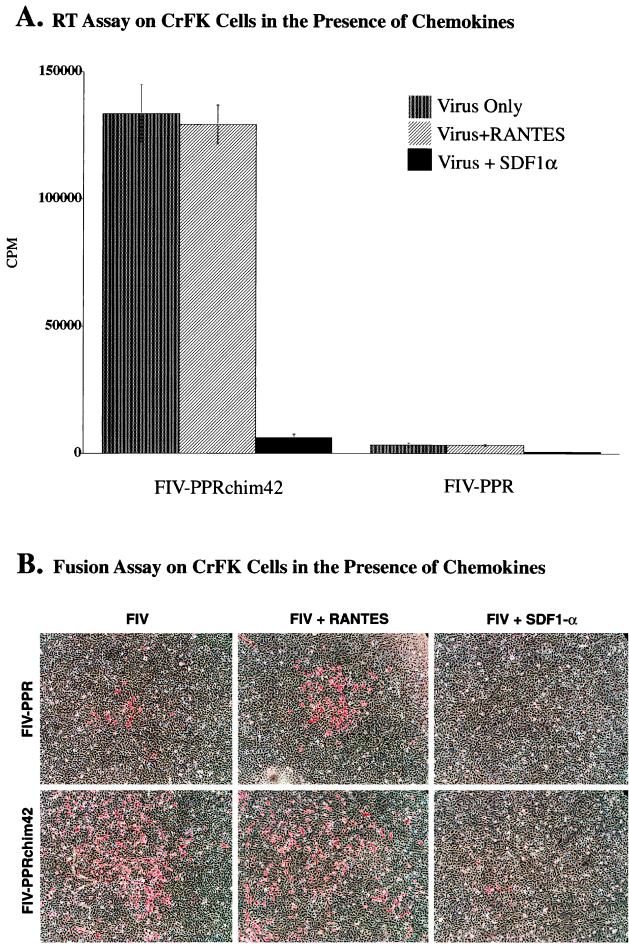
FIG. 5.
Results from chemokine inhibition assays on CrFK cells infected with FIV-PPR and FIV-PPRchim42. (A) Graphic representation showing the low-level infection of FIV-PPR infection upon adherent cells and the contrasting highly productive infection of CrFK by FIV-PPRchim42. The panel also shows the nearly complete inhibition of FIV-PPRchim42 and FIV-PPR in the presence of SDF1α, indicating that these viruses utilize CXCR4 for entry. RANTES had no effect on the infections. (B) Immunocytochemical analyses of FIV-PPR and FIV-PPRchim42 infections on CrFK cells in the presence of chemokines. FIV-PPR infection is readily detected by this method, whereas the infection is below the level of sensitivity of the RT assay, as observed in panel A. Also, the foci of infection were enlarged in the FIV-PPR infections in the presence of RANTES and the foci were sparse compared with those observed with FIV-PPRchim42, which were not limited to focal points. Importantly, it was observed that SDF1α was able to severely inhibit the infections correlating with the RT data presented in panel A.