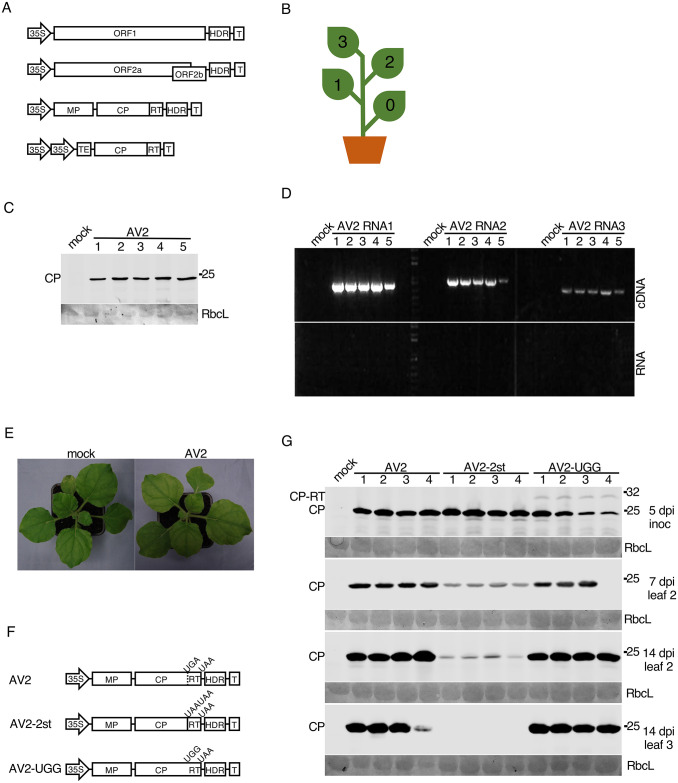
Fig 3. Testing the infectivity of the AV2 full-length cDNA clone in N. benthamiana and mutagenesis of the RT domain.
(A) Schematic representation of the AV2 cDNA infectious clone. The full-length cDNAs of the AV2 genomic RNAs 1, 2 and 3 were inserted independently into pDIVA between the CaMV 35S promoter (35S) and a hepatitis delta ribozyme sequence (HDR) followed by a transcription terminator (T). The cp-rt coding sequence (including the CP stop codon) was inserted independently into pLH 7000 between double 35S promoters followed by the tobacco etch virus translational enhancer (TEV) at the 5′ end, and a transcription terminator (T) at the 3′ end. (B) Schematic representation of an infected N. benthamiana plant with indicated leaf positions where 0 indicates the inoculated leaf. (C,D) Detection of AV2 in the 3rd upper non-inoculated leaf at 21 dpi for five infected plants by western blot against CP (panel C), and RT-PCR with primers for detection of RNAs 1, 2 and 3 (panel D). PCR on RNA without a reverse transcription step (panel E, bottom) served as a negative control. (E) Lack of visible symptoms on the upper non-inoculated leaves of a representative AV2-infected N. benthamiana plant (right) compared to a mock-inoculated plant (left). (F) Schematic representation of AV2 RNA3 mutants. (G) Detection of AV2 CP by western blot in plants infected with AV2, AV2-2st or AV2-UGG. Samples were collected from the inoculated leaf at 5 dpi, the 2nd non-inoculated leaf at 7 and 14 dpi, and the 3rd non-inoculated leaf at 14 dpi. Positions of CP and CP-RT are indicated on the left. In panels C and G, sizes of molecular weight markers are indicated on the right, and Ponceau red staining (lower panels) was used as a loading control.