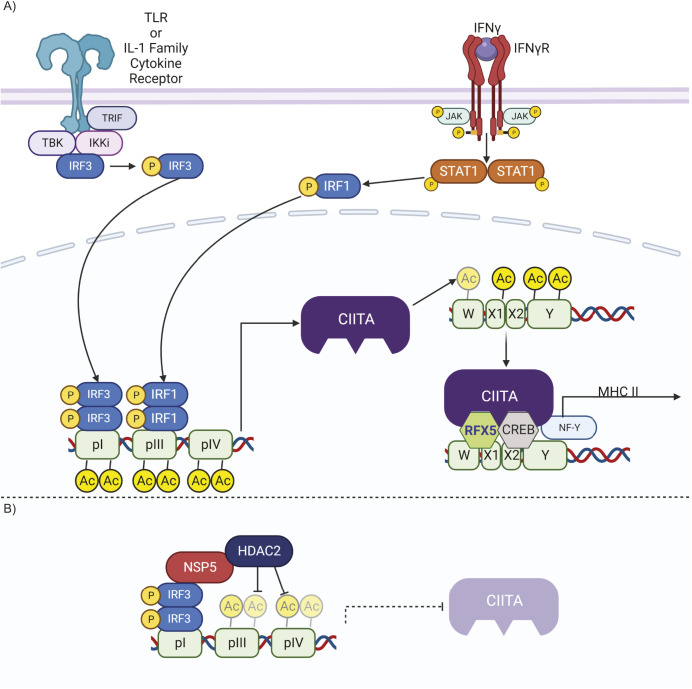
Fig. 7.
Model of MHC II transcriptional control and NSP5 activity at the MHC II promoter. (A) MHC II expression in myeloid cells is induced by a combination of IFN-γ and STAT1 together with TLR or IL-1 family cytokine signaling, which respectively activate IRF1 and IRF3. IRF1 and IRF3 then bind to the CIITA promoter and induce CIITA expression (left). Once synthesized, CIITA directly acetylates histones in the MHC II promoter via its intrinsic acetyltransferase activity. Once the MHC II promoter is acetylated, CIITA, RFX5 and NF-Y form an activating complex on the W, X1, X2 and Y motifs found in the core of the MHC II promoter, inducing expression of MHC II (right). (B) During SARS-CoV-2 infection, NSP5 binds to HDAC2, and via interactions with IRF3, delivers HDAC2 to the CIITA promoter. Here, HDAC2 deacetylates and inactivates the CIITA promoter, thereby suppressing the expression of CIITA, with the resulting loss of CIITA then leading to the cessation of MHC II expression. Figure produced in BioRender.