Fig. 5. Visual-dependent behavioral assessment of rats that underwent cell therapies with Morris water maze.
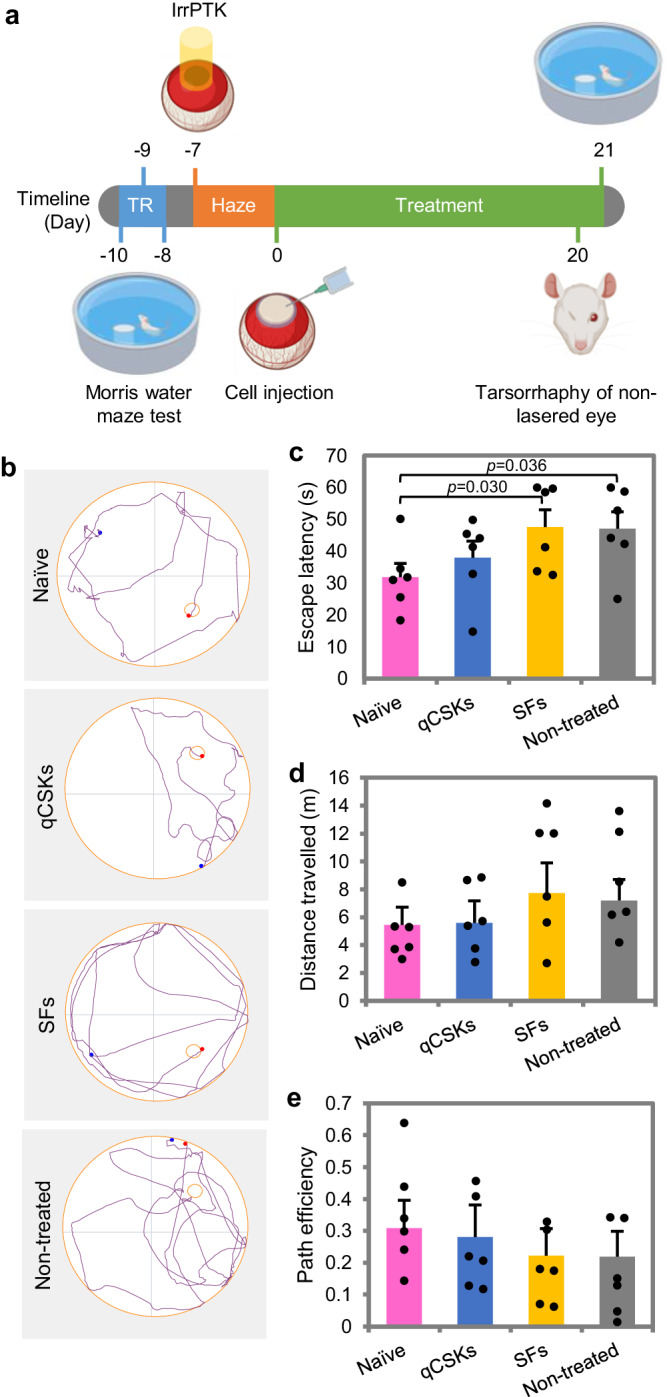
a Experimental timeline showing the swim training regime (TR), acute corneal haze induction with irregular phototherapeutic keratectomy (IrrPTK) and haze development, cell therapy, and closure of the eyelid of the non-lasered eye a day before the final test. b The swim path maps indicated that naïve and quiescent corneal stromal keratocytes (qCSKs)-treated rats performed better, e.g., traveled a shorter distance from the start point (black spots) to the escape platform (red spots) than the stromal fibroblasts (SFs) and non-treated groups. The qCSK-injected rats (blue bars) displayed similar escape latency (c), distance traveled (d), and path efficiency (e) as the naïve rats (pink bars). On the other hand, the SFs-treated (yellow bars) and non-treated (gray bars) rats had higher escape latency and distance traveled, and lower path efficiency than the naïve rats. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6 rats in each group, with each rat subjected to the trial thrice). Statistical significance was analyzed with one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc Tukey test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
