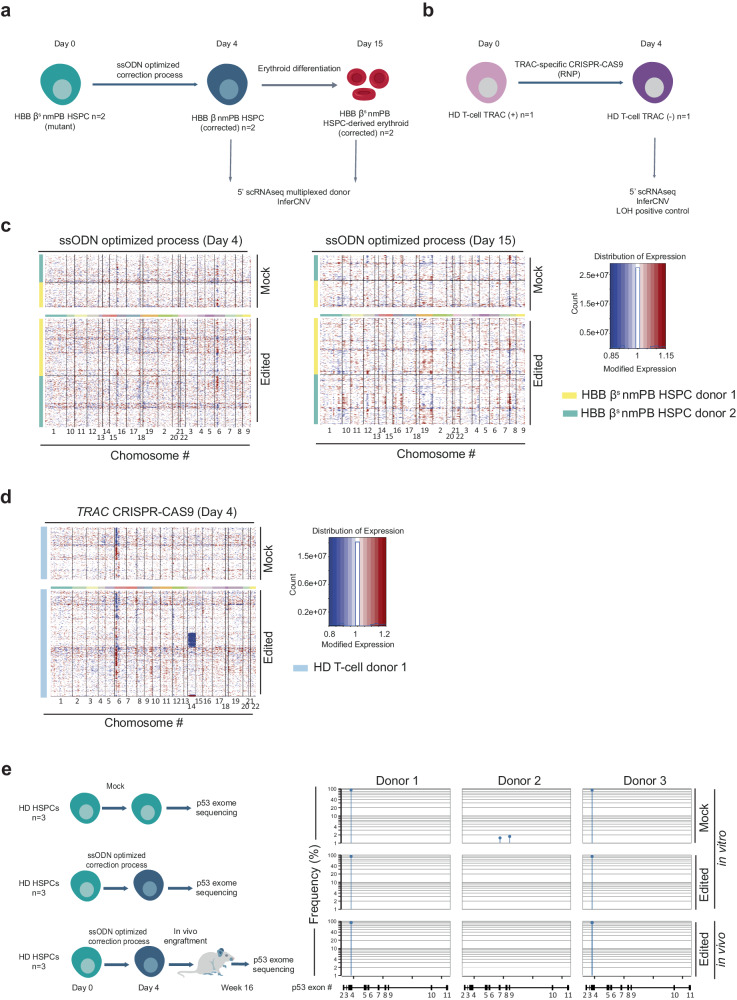
Fig. 8. Characterization of TALEN-mediated genomic adverse events after optimized non-viral editing at HBB locus in HSPCs.
a Representative schema of scRNAseq InferCNV analysis performed to identify the potential large genomic rearrangement including gain and loss of heterozygosity in HSPC, n = 2 HbSS donors transfected with mRNA encoding TALEN-HBBss, Via-Enh01, HDR-Enh01 and with ssODN. b Representative schema of experimental design to verify the ability of scRNAseq InferCNV to detect loss of heterozygosity in T-cells. c scRNAseq InferCNV InferCNV results obtained from samples gathered 4 days post HSPC thawing (Day 4) and after erythroid differentiation (Day 15). Each individual row corresponds to a single cell and each column corresponds to a specific gene and its genomic position, grouped by chromosome. Red color represents increase in gene expression, while blue color represents decrease in gene expression. d scRNAseq InferCNV results obtained from T-cell sample edited by TRAC-specific CRISPR-CAS9 and gathered 4 days post editing (Day 4). The color code is similar as in (c). Typical examples of LOH are illustrated by the blue lines seen across chromosome 14, where the TRAC CRISPR-CAS9 is designed to cut. e P53 exome sequencing obtained from the genomic DNA of untouched HD HSPCs (mock in vitro) or of HD HSPCs edited by the optimized non-viral gene editing process and gathered 4 days post editing (edited in vitro) or 16 weeks after NCG mice engraftment onset (edited in vivo). The frequency and exonic position of p53 variants obtained in each donor (n = 3 independent biological experiments and donors) and in each experimental group are indicated. The detection threshold was set to 1% according to the p53 exon sequencing kit’s manufacturer guidelines. The p53 variant identified in the mock and edited experimental groups of donors 1 and 3 corresponds to a natural single nucleotide variant frequently identified in healthy donors (rs1042522, worldwide median prevalence of 66.4%, Supplementary Fig. 7b).