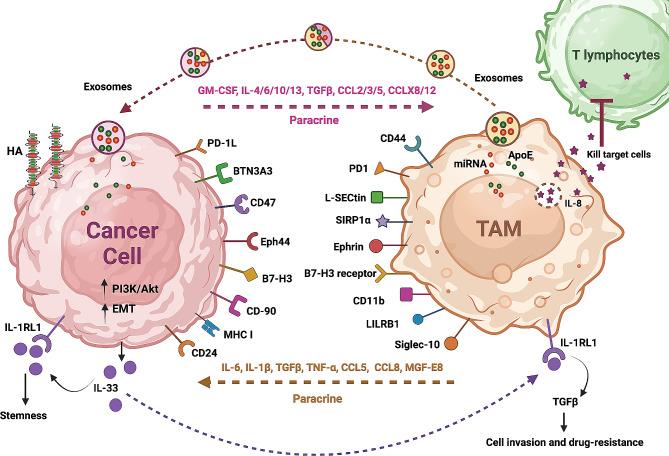
Fig. 2.
Crosstalk between tumour cells and tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs). TAMs secrete chemokines and cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10, which actively contribute to cancer advancement. Notably, IL-8 released by TAMs exerts cytotoxic effects on T lymphocytes. Additionally, various juxtacrine interactions between tumour cells and TAMs play a pivotal role in inducing immunosuppression. The PD-1/L1 signalling pathway further exacerbates tumour immune evasion by impeding the normal functioning of macrophages and other immune effector cells. Furthermore, the interaction of B7-H3 with its receptor has been implicated in the inhibition of T lymphocytes, thus facilitating tumour immune evasion. The SIRPα/CD47 and CD24/Siglec-10 pathways serve as the “do-not-eat-me” signal, wherein tumour cells over-expressing CD47 and CD24 are recognized as self-normal cells, thereby evading phagocytosis by macrophages. Another significant mechanism of tumour evasion involves LILRB1/MHC class I component β2-microglobulin, which inhibits the phagocytosis of tumour cells by macrophages. Exosomes facilitate intercellular communication by transporting various molecules, including exosomal mRNA, circRNA, lncRNA, miRNA, lipids, and proteins. Interestingly, exosomes exhibit dynamic alterations in their cargo during transit from the origin to the destination cell. ApoE is highly expressed in TAMs and is transferred, along with other molecules, via exosomes to cancer cells, activating the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway and promoting cytoskeletal remodeling, EMT, and cancer cell migration. Other juxtacrine mechanisms, such as Eph44-ephrin interaction, regulate immune cell processes, including proliferation, survival, apoptosis, activation, and migration. CD44, a transmembrane adhesion molecule, plays a crucial role in binding and metabolizing hyaluronic acid (HA) and serves as an effective phagocytic receptor, influencing inflammation, phagocytosis, and multi-drug resistance. Interactions such as CD44-HA, BTN3N3–L-SECtin, CD90-CD11b, and Eph44-ephrin also also trigger signals that support the maintenance of cancer stem cells. Furthermore, IL-33 released by tumour cells sustains stemness via autocrine interaction with IL-1RL1, while also promoting tumour cell invasion and drug resistance through TAM-mediated TGF-β release and TAM proliferation and differentiation in a paracrine manner. This intricate interplay results in the amplification of the aforementioned crosstalk. Abbreviations: Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), C-C motif chemokine Ligand, (CCL), circular RNA (circRNA), epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), hyaluronic acid (HA), interleukin (IL), Janus kinase (JAK), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MGF-E8), major histocompatibility complex (MHC), microRNA (miRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF⍺)