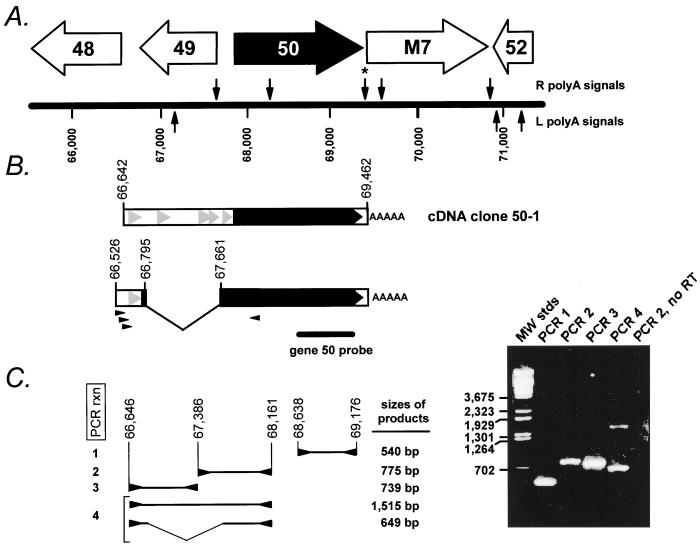
FIG. 2.
(A) Schematic illustration of the gene 50 region of the γHV68 genome (39). The locations of the putative viral genes adjacent to gene 50 are indicated, as are the locations of consensus poly(A) signals, which are indicated above (for those associated with the R strand of the viral genome) and below (for those associated with the L strand of the viral genome) the map of the viral genome. The asterisk denotes the poly(A) signal which was utilized in the transcript from which the cDNA clone 50-1 was generated. (B) Schematic structure of the cDNA clone 50-1, which is unspliced and contains viral sequences from bp 66642 to 69462. Below the schematic of the cDNA clone 50-1 is the deduced structure of the ∼2.0-kb spliced gene 50 transcript, based on RT-PCR analysis (see discussion in text). The small arrowheads below the spliced transcript denote PCR primers used to amplify the spliced form of the gene 50 cDNA. Also shown is the position of the gene 50 probe used in the Northern blot shown in Fig. 1. The solid black arrow indicates the gene 50 open reading frame, which is extended by the splice to the upstream exon, as illustrated in Fig. 3. The grey arrowheads indicate the presence of small (encoding >25 amino acids) open reading frames upstream of gene 50. (C) RT-PCR analysis of gene 50 transcripts. The structures and sizes of the RT-PCR products obtained employing the indicated PCR primers (arrowheads) are shown to the left of the ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel. The viral genomic coordinates (39) of the PCR primers employed for each reaction were as follows: PCR 1, upstream primer bp 68638 to 68660 and downstream primer bp 69176 to 69154; PCR 2, upstream primer bp 67386 to 67407 and downstream primer bp 68161 to 68141; PCR 3, upstream primer bp 66646 to 66667 and downstream primer bp 67385 to 67364; and PCR 4, upstream primer bp 66646 to 66667 and downstream primer bp 68161 to 68141. Also shown is an ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of the PCR products generated with the primers indicated. A negative control RT-PCR, to detect the presence of contaminating viral genomic DNA in the RNA preparation, is shown (primers for PCR 2 were used to amplify DNA present in a cDNA synthesis reaction lacking reverse transcriptase [PCR 2, no RT]). All the PCR products visible by ethidium bromide staining were cloned and sequenced.