Figure 3.
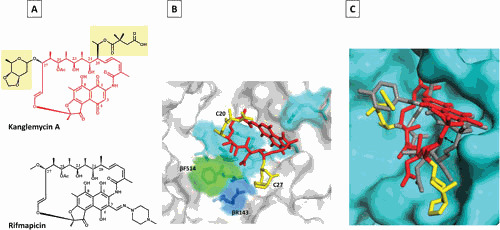
Mode of KglA binding to RNAP compared with RMP. (A) Chemical structures of KglA (in red with C-20 and C-27 side chains highlighted in yellow) and RMP (black). (B) A close-up view of KglA in the RIF-binding pocket of T. thermophilus RNAP (PDB: 6CUU). KglA is shown as a stick model (red) with its deoxysugar and succinate groups shown in yellow. RNAP is shown as a transparent surface model (gray), and RNAP β residues, which form the RIF-binding pocket, are shown as stick models. KglA binds to the same residues that RMP binds (cyan) to, with the exception of βF514 (green). KglA makes additional binding with βR143 (blue). (C) A side view of KglA in the RIF-binding pocket shown in panel B (PDB: 1YNN and 6CUU). The RNAP β subunit is shown in cyan. KglA (red and yellow) is overlaid on RMP (gray). Compared with RMP, KglA maintains a larger distance from the RIF-binding pocket (depicted by the two-headed arrow) (41).
