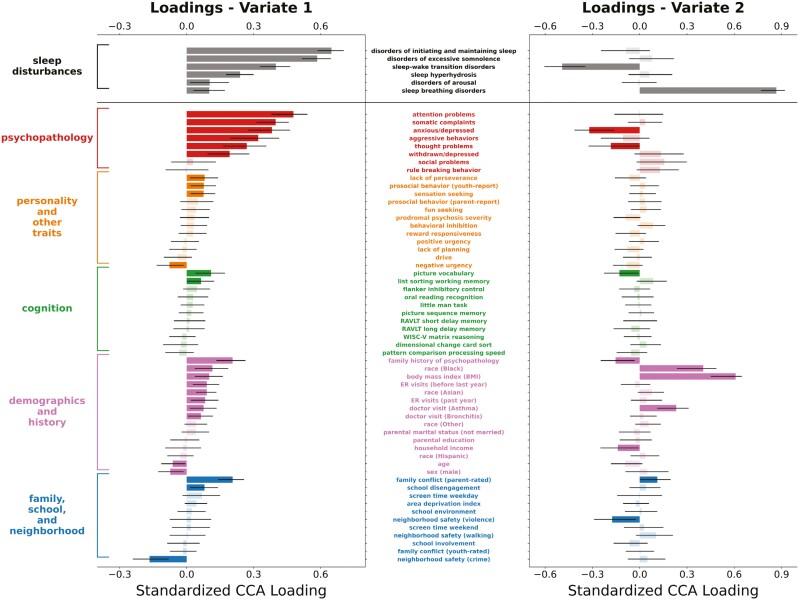
Figure 2.
Plots of standardized loadings of CCA analysis relating sleep disturbances and multidomain predictors in the ABCD study baseline data. We used a multivariate machine learning method, CCA, to delineate associations between sleep disturbances on the one hand and a number of predictor domains on the other (i.e. psychopathology; personality and other traits; cognition; demographics and history; and family, school, and neighborhood). The y-axis lists the predictor variables (middle) and their respective domains (left), and the x-axis shows standardized beta weight values for these predictors. Error bars represent the 95% CI based on bootstrap analysis. Statistical significance is indicated by darkly shaded bars. For the first CV (left column), multidomain psychopathology was the strongest predictor of difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep and excessive daytime somnolence. For the second CV (right column), BMI and African American/black race were strongly predictive of sleep breathing disorders. Abbreviations: CCA, canonical correlation analysis; RAVLT, Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test; WISC-V, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-5th Edition; ER, emergency room.