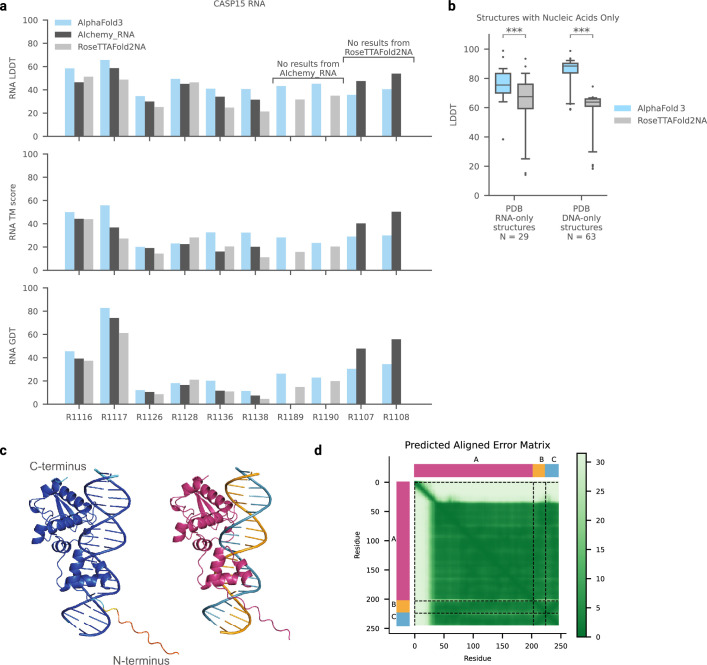
Extended Data Fig. 5. Nucleic acid prediction accuracy and confidences.
a, CASP15 RNA prediction accuracy from AIChemy_RNA (the top AI-based submission), RoseTTAFold2NA (the AI-based method capable of predicting proteinRNA complexes), and AlphaFold 3. Ten of the 13 targets are available in the PDB or via the CASP15 website for evaluation. Predictions are downloaded from the CASP website for external models. b, Accuracy on structures containing low homology RNA-only or DNA-only complexes from the recent PDB evaluation set. Comparison between AlphaFold 3 and RoseTTAFold2NA (RF2NA) (RNA: N = 29 structures, paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 1.6 * 10−7; DNA: N = 63 structures, paired two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 5.2 * 10−12). Note RF2NA was only trained and evaluated on duplexes (chains forming at least 10 hydrogen bonds), but some DNA structures in this set may not be duplexes. Box, centerline, and whiskers boundaries are at (25%, 75%) intervals, median, and (5%, 95%) intervals. c Predicted structure of a mycobacteriophage immunity repressor protein bound to double stranded DNA (PDB ID 7R6R), coloured by pLDDT (left; orange: 0–50, yellow: 50–70, cyan 70–90, and blue 90–100) and chain id (right). Note the disordered N-terminus not entirely shown. d, Predicted aligned error (PAE) per token-pair for the prediction in c with rows and columns labelled by chain id and green gradient indicating PAE.