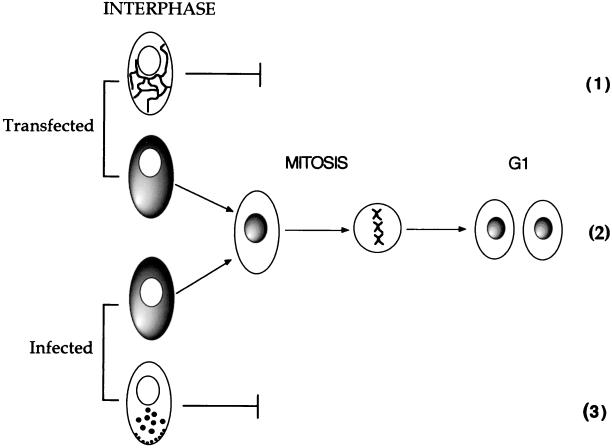
FIG. 8.
Model for the compartmentalization of VP22 through the cell cycle. In both transfected and infected cells, we propose that VP22 localizes primarily to the cytoplasm of interphase-expressing cells. If such a cell enters mitosis, VP22 translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and remains there through chromatin decondensation and nuclear envelope reformation (2). However, in both transfected and infected cells mitosis may be inhibited either by VP22-induced microtubule bundling (1) or by later stages in virus replication (3).