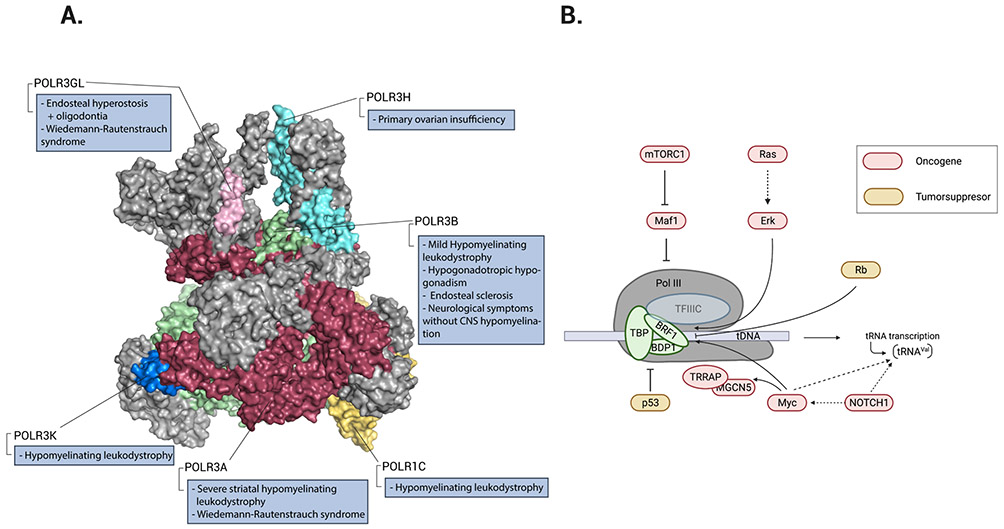
Figure 2. RNA polymerase III involvement in disease.
a ∣ Structure of RNA polymerase III (Pol III) (Protein Data Bank entry 7AST)23. The colours identify Pol III subunits that harbour pathological mutations in humans. b ∣ The regulatory effect of oncoproteins (red) and tumour suppressors (yellow) on Pol III-mediated transcription of tRNA genes. The three subunits of TFIIIB: TATA-box-binding protein (TBP), B double prime 1 (BDP1), and B-related factor-1 (BRF1), are shown interacting with TFIIIC. mTORC1 indirectly stimulates Pol III transcription via inhibition of MAF1, a negative regulator of Pol III. Ras small GTPases activate their downstream effector extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), which induces BRF1 expression. Rb binds directly to BRF1, which inhibits Pol III recruitment. NOTCH1 stimulates tRNAVal transcription both directly and via targeting MYC. MYC directly interacts with BRF1 and activates the histone-modifying enzymes transformation and transcription domain-associated protein (TRRAP) and GCN5. P53 directly inhibits TBP and Pol III recruitment. Part a is adapted from ref23.