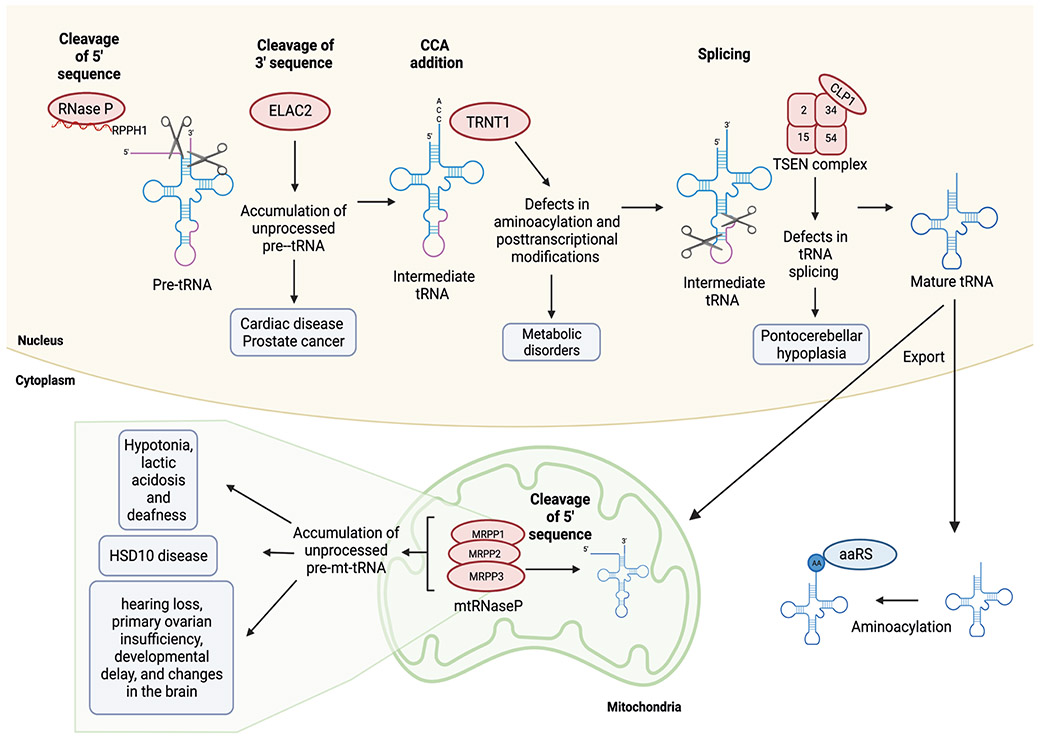
Figure 4. tRNA maturation and splicing defects in disease.
tRNA maturation involves the removal of 5' leader and 3' trailer sequences, CCA addition, and in some instances splicing of a short intron. Subsequently the mature tRNA is exported to the cytoplasm for aminoacylation (AA) by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (aaRS). Some nuclear encoded tRNAs are imported into mitochondria. Mutations in proteins involved in the maturation of tRNAs (red) can lead to disease (shaded boxes). Levels of ribonuclease P (RNAse P) and ribonuclease P RNA component 1 (RPPH1) enzymes are increased in cancer but the physiological relevance of these alterations remains unknown.