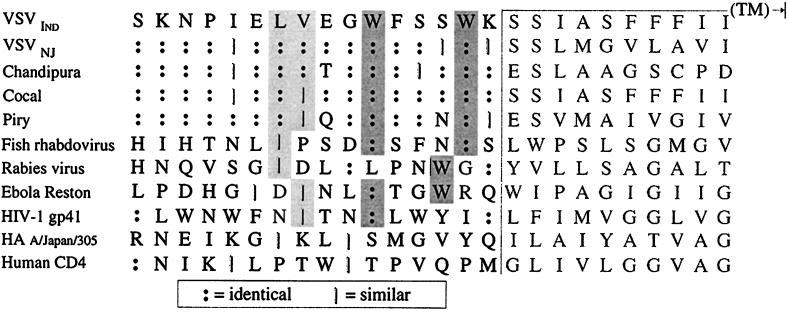
FIG. 7.
Sequence alignment of the TM-ectodomain junction of VSV G protein with analogous regions of related and unrelated type I glycoproteins. Darkly shaded boxes indicate conserved tryptophan residues within the membrane-proximal regions of the glycoprotein ectodomains which are spaced either two or three residues and/or six residues from the putative TM domain. Lightly shaded boxes indicate hydrophobic residues positioned at either the third, fourth, or seventh residue from the conserved tryptophans. A high degree of sequence homology within their membrane-proximal regions is observed for related vesiculovirus glycoproteins, whereas the glycoproteins of a fish rhabdovirus (hemorrhagic septicemia virus, an unclassified rhabdovirus), RV (a lyssavirus), ebola virus (a filovirus), and HIV-1 (a lentivirus) are similar to VSV G only in that these have a similar spacing of tryptophan and hydrophobic residues at a conserved distance from their TM domains.