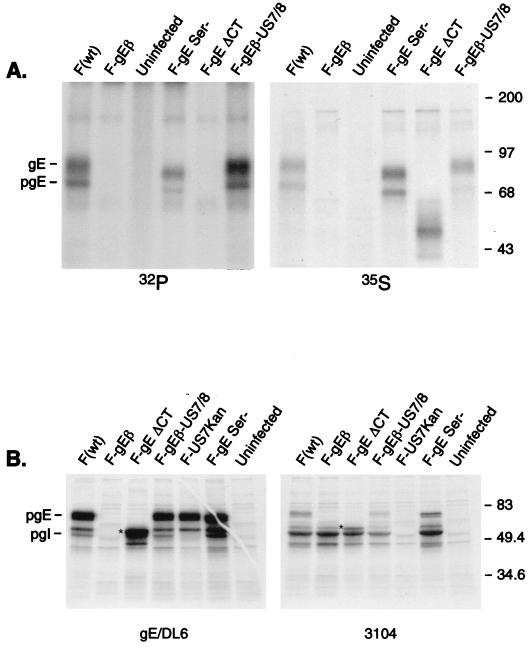
FIG. 3.
Expression of mutant forms of gE, binding to gI, and phosphorylation. (A) R-970 cells were infected with wild-type HSV-1 (strain F), F-gEβ, F-gESer, F-gEΔCT, or F-gEβ-US7/8 for 7 h. The cells were then radiolabeled for 3 h with [32P]orthophosphate or [35S]methionine/cysteine. Detergent extracts of the cells were made and gE was immunoprecipitated after a mild denaturation step (so that the gE/gI complex was disrupted) using anti-gE MAb II-481. (B) HEC-1A cells were infected for 7 h with the same viruses described for panel A, as well as F-US7Kan, a gI mutant. The cells were labeled for 30 min with [35S]methionine/cysteine and gE immunoprecipitated using anti-gE/DL6, an anti-gE rabbit serum, or gI immunoprecipitated using MAb 3104. The positions of gE and pgE, as well as molecular mass markers, are indicated. The ΔCT gE protein is indicated by a star, and gI migrates just slightly slower.