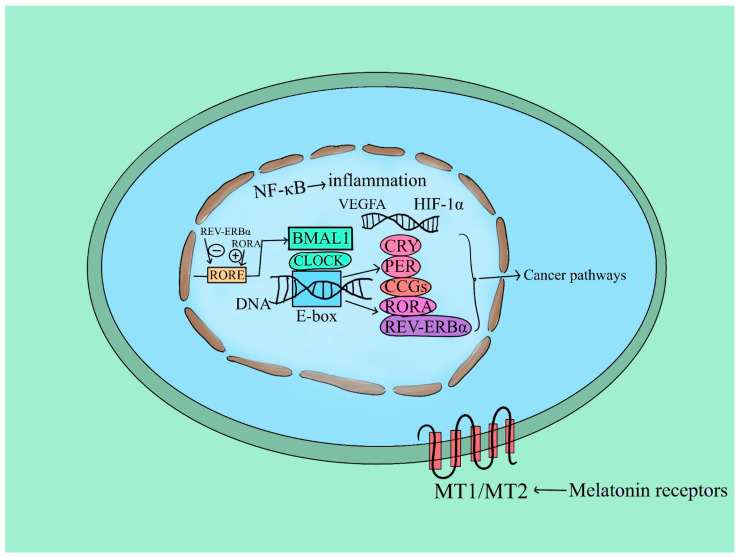
Figure 4.
Disrupted circadian rhythm and molecular pathways in the development of cancer. By blocking NF-κB and HIF1α from translocating to the nucleus, melatonin inhibits pathways related to survival and inflammation via binding to the MT1 and MT2 receptors. To activate the transcription of clock-controlled genes (CCGs), RORα, REV-ERBα, CRY (1-2), PER (1-3), and BMAL1 and CLOCK heterodimerize and bind to the E-box. BMAL and CLOCK heterodimer inhibition by CRY and PER creates the main negative feedback loop. BMAL1’s transcription is inhibited by REV-ERBα, while RORα is activated in the secondary feedback loop.