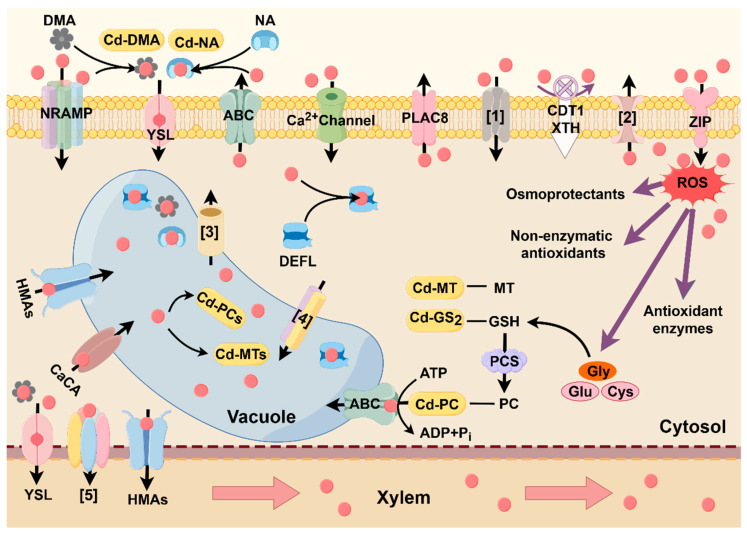
Figure 3.
Schematic model of the major proteins/enzymes that are absorbed, transported, sequestered, and detoxified in plants. Red circles represent Cd2+ and [number] represents the serial number. Plants take up Cd and Cd chelates through NRAMP, YSL, ZIP families, and Ca2+ channels; ABC and PLAC8 families have been shown to function in effluxing Cd out of the plant; CDT1 and XTH can avoid Cd entry by binding Cd or by reducing the Cd-binding site; the DEFL family can bind to Cd and convert Cd ions into stable compounds; HMA, CaCA, and ABC families can transport Cd and chelates into vacuoles to alleviate the toxic effects; YSL and HMA can transport some Cd to xylem and transfer it to the aboveground part. Refs. [1,2,3,4,5] are proteins that have been reported to be related to Cd transport. Ref. [1] SpHMA6, SaPCR2, SlCNR8, PcPLAC8-10, OsCd1, OsHIR1, OsAAN4, and OsGLR3.4, respectively; Ref. [2] SlCNR8, OsZIP1, OsHMA9, HaMTP10, AtPDF2.5, OsCCX2 (OsCDT1), OsLCT1; Ref. [3] OsNRAMP2, AtNRAMP3, AtNRAMP4; Ref. [4] TmMTP1, TmMTP11, AtCAX2; Ref. [5] OsZIP7, OsCAL1. On the right is the Cd-induced ROS scavenging cycle. Cd enters the cytoplasm and stimulates the synthesis of osmoprotectants, antioxidants, glutathione and phytochelatin, and metallothionein. MT, GSH, and PC can bind to Cd to generate Cd-GS2, Cd-MT, and Cd-PC to alleviate the toxicity of Cd caused to the cells. ROS, reactive oxygen species; NRAMP, natural resistance-associated macrophage protein; YSL, yellow-stripe-1-like; ABC, ATP-binding cassette family; PLAC8, the placenta-specific 8-domain-containing family; ZIP, ZRT-IRT-like protein family; zinc-regulated; HMA, heavy metal ATPase; CaCA, cation/calcium superfamily; DEFL, defensin-like protein family; PCS, phytochelatin synthetase; Gly, Glycine; Glu, Glutamate; Cys, Cysteine; MT, metallothioneins; GSH, glutathione; PC, phytochelatin; NA, nicotianamine; DMA,2’-deoxymugineic acid.