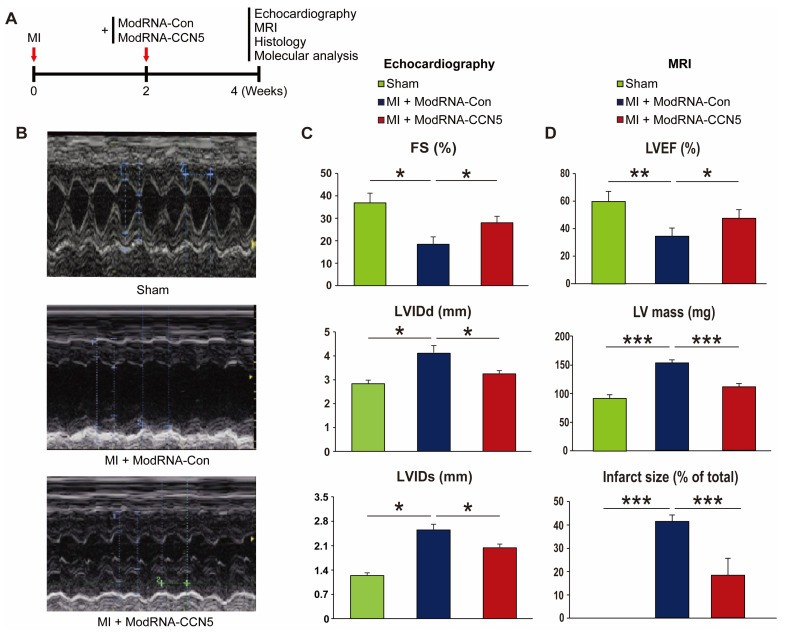
Figure 3.
Therapeutic intervention of ModRNA-CCN5 mitigates MI-induced cardiac dysfunction. (A) MI was induced in the heart. Then, 2 weeks later, ModRNA-Con or -CCN5 was directly injected into the endocardium of the mouse LV (therapeutic intervention). Subsequently, 4 weeks later, echocardiography, MRI, histology, and molecular analysis were performed to determine the effects of modified mRNA-CCN5. (B) Representative M-mode echocardiographic images are shown. (C) Fractional shortening (FS), LVIDd, and LVIDs were compared, sham (n = 7) vs. MI + ModRNA-Con (n = 7) vs. MI + ModRNA-CCN5 (n = 8). (D) MRI was performed in each group of mice (n = 3 for sham, n = 4 for ModRNA-Con, and n = 4 for ModRNA-CCN5) and some critical values are presented. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), LV mass, and infarct size were compared, sham vs. MI + ModRNA-Con vs. MI + ModRNA-CCN5. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.