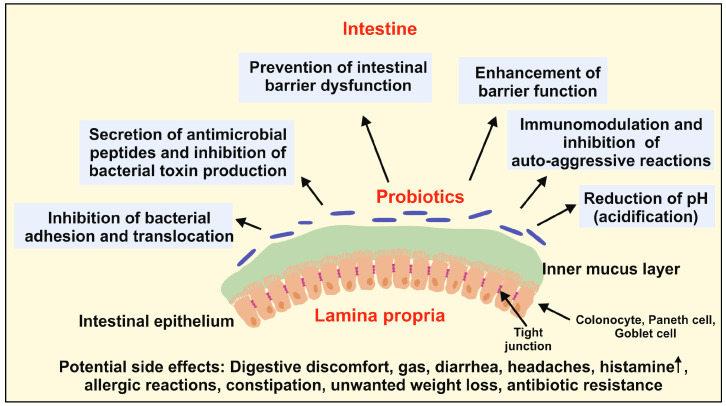
Figure 3.
Beneficial effects of probiotics on the function and homeostasis of the intestinal barrier. Probiotics impact the intestinal barrier by preventing intestinal barrier dysfunction through enhancing the expression of tight junction proteins and inhibition of bacterial adhesion and translocation. Moreover, probiotics lower the luminal pH value through the secretion of anti-microbial active peptides, acetic and lactic acids, which inhibits the growth of non-commensal pathogens and the production of their bacterial toxins. They further modulate the host’s immune system, thereby inhibiting auto-aggressive reactions. However, probiotics can have the depicted side effects such as digestive discomfort, headaches, constipation, unwanted weight loss, and others. Please note that the image does not show the full structure of the gastrointestinal wall including its mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.