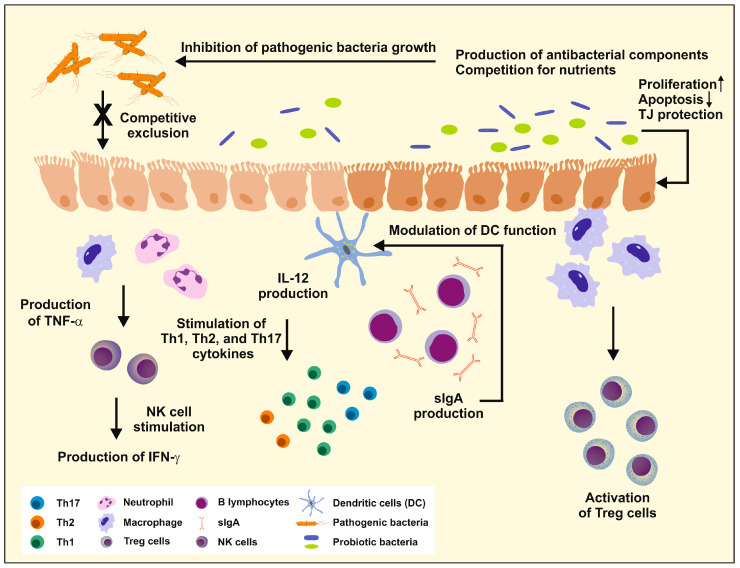
Figure 4.
Probiotics are effective in strengthening the host’s immune system. They have various effects on an individual’s health, including inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria through the production of antibacterial components and competition for nutrients. Probiotics also compete for mucosal adhesion sites and stimulate the expression of cytokines that affect cell proliferation and apoptosis. Additionally, they promote the production of tight junction (TJ) proteins and stimulate or modulate immune cell function in natural killer (NK) cells and dendritic cells (DC). The increased production of secretory IgA (sIgA) helps protect the intestinal epithelium from enteric pathogens and their toxins. More information on the impact of probiotics on immunity and their mechanism of action on immune cells can be found in other publications [62,63]. Please note that the gastrointestinal wall is only roughly depicted and does not show its fine structure, which includes the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.