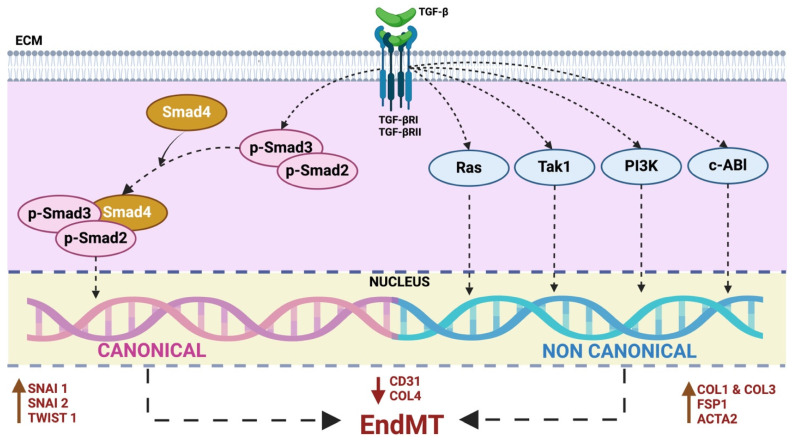
Figure 3.
Canonical and noncanonical TGF- β signaling in EndMT. TGF-β homodimers interact with the TGF-β I/II receptor complex on the cell surface to initiate the canonical TGF-β pathway. This triggers the phosphorylation and activation of Smad2 and Smad3 proteins. Subsequently, the activated Smad2/3 complex with Smad4 translocate to the nucleus and activate transcription of genes involved in creating profibrotic extracellular matrix components such as Col4, Col1, Col3 and transcription factors like Snai1, Snai2, and Twist1. Noncanonical pathways involving kinases PI3K, Tak1, Ras, and c-Abl also influence EndMT. These pathways can lead to different cellular responses, independent of Smad2/3 activation, either by decreasing endothelial-specific gene transcription or increasing mesenchymal-specific gene expression. These pathways impact the expression of genes associated with EndMT, leading to variations in the transcription of markers like CD31, Col4, Col1, Col3, FSP1, and Acta2. Notably, these effects are also influenced by transcription factors such as Snai1, Snai2, and Twist1. TGF-β: Transforming Growth Factor-β, ECM: Extracellular Matrix, TGF-βRI/II: Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I/II, EndMT: Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, Col4: Collagen Type IV, Col1: Collagen Type I, Col3: Collagen Type III, PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Tak1: TGF-β-activated kinase 1, c-Abl: Abelson Tyrosine-Protein Kinase 1, CD31: Cluster of Differentiation 31, FSP1: Fibroblast-Specific Protein 1, Acta2: Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin, Snail1: Zinc Finger Protein SNAI1, Snail2: Zinc Finger Protein SNAI2, Twist: Twist Family BHLH Transcription Factor 1.