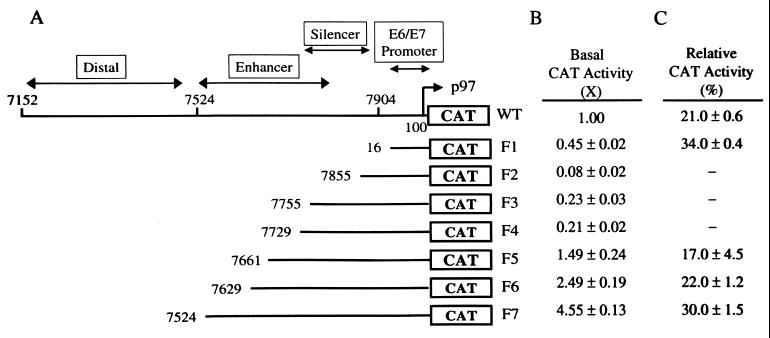
FIG. 3.
Identification of motifs on the HPV-16 LCR involved in AAV-induced inhibition of promoter activity by mutation analyses. (A) Constructs of the WT and mutant (F1 to F7) HPV-16 LCR. The mutated LCR fragments were produced by PCR as outlined in Table 1 and were subsequently cloned into the vector pBLCAT6. (B) Promoter activities of WT and mutated HPV-16 LCR constructs. SiHa cells were cotransfected with 10 μg of reporter plasmid containing the WT or one of the mutated LCR constructs. The basal CAT activity from cells transfected with the WT construct was defined as 1, and the CAT activity from cells transfected with mutant LCR constructs is reported relative to that of the WT LCR. (C) Inhibitory effects of AAV on the promoter activities of WT and mutated HPV-16 LCR constructs. SiHa cells were cotransfected with 10 μg of a reporter construct carrying the WT or one of the truncated LCR fragments along with pAV1 or pBR322. The HPV/AAV molar ratio used for cotransfection was 2:1. pBLCAT6 and pSV2CAT were used as negative and positive controls, respectively (data not shown). −, not done. The results are reported as percentages of the value relative to the activity of samples from cells transfected with the same LCR construct plus pBR322. The data are the means ± standard errors of three individual experiments.