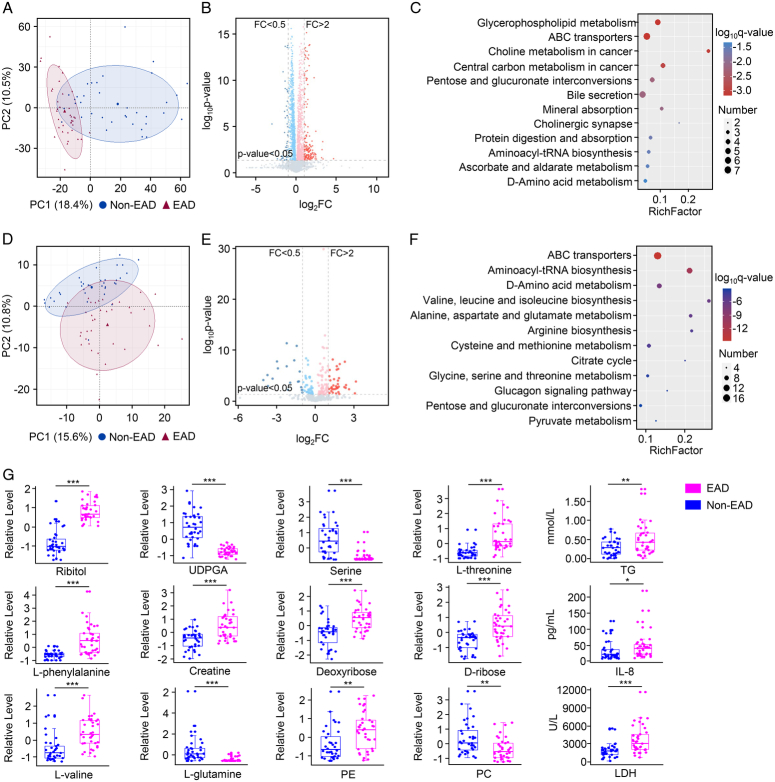
Figure 3.
Perfusate metabolomic features of EAD. (A) Principal component analysis plot of the EAD and non-EAD groups in LC–MS-metabolomics. (B) The volcano plot for the DEMs in LC–MS-metabolomics. Red represented FC >2 and P<0.05; blue represented FC <0.5 and P<0.05. (C) KEGG pathway analysis between the EAD and non-EAD groups in LC–MS-metabolomics. (D) Principal component analysis plot of the EAD and non-EAD groups in GC–MS-metabolomics. (E) The volcano plot for the DEMs in GC–MS-metabolomics. Red represented FC >2 and P<0.05; blue represented FC <0.5 and P<0.05. (F) KEGG pathway analysis between the EAD and non-EAD groups in GC–MS-metabolomics. (G) The representative differential expressed metabolic products between the EAD and non-EAD groups (***P<0.001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05). DEMs, differentially expressed metabolites; EAD, early allograft dysfunction; FC, fold change; IL-8, interleukin-8; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphorylethanolamine; TG, triglyceride; UDPGA, UDP glucuronic acid.