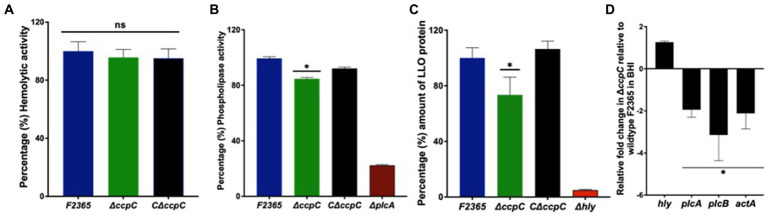
Figure 1.
The hemolytic activity, phospholipase activity, and intracellular replication of the ΔccpC and wildtype F2365. (A) Percentages of hemolytic activity in sheep erythrocytes by ΔccpC strain showed non-significant ~2% reduction in hemolytic activity compared to the wildtype F2365 (p > 0.05). (B) The ΔccpC strain exhibited ~20% reduction in phospholipase activity compared to the wildtype F2365 strain when examined on BLA plates containing lecithin (p < 0.05). The C∆ccpC partially restored the phospholipase activity with opacity zone size similar to F2365. (C) The ΔccpC strain on western blot showed a significantly reduced LLO protein level (~25%) compared to the wildtype F2365 (p < 0.05), while the C∆ccpC restored the amount of LLO protein to the wildtype F2365 level. (D) The effect of ccpC deletion on the relative expression of plcA, plcB, actA, and hly during the growth of L. monocytogenes strains in BHI broth using RT-qPCR. The expression of plcA, plcB, and actA genes was significantly downregulated in the ΔccpC strain compared to the wildtype F2365 (p < 0.05), whereas hly gene was insignificantly upregulated (p > 0.05). Bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) of six replicates. The data were compared with Student’s t-tests. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences, p < 0.05. NS, No significant difference.