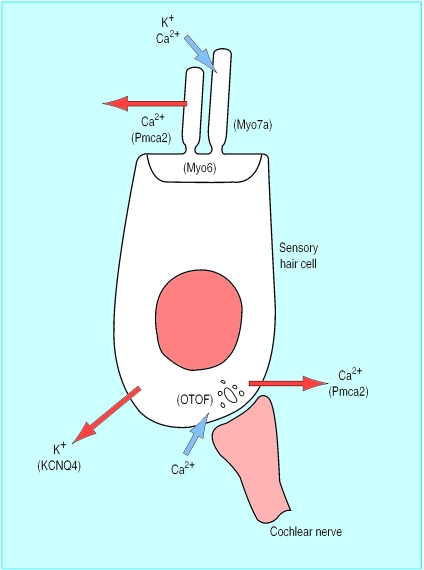
Figure 2.
Diagram of sensory hair cell and some of the molecules associated with deafness. Sound causes deflection of stereocilia (“hairs”) at top of cell, opening transduction channels in cell membrane and allowing potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+) ions to enter and depolarise cell, which triggers release of neurotransmitters at synapse at base of cell and initiates action potential in cochlear nerve. Three motor molecules—encoded by genes Myo6, Myo7a, and Myo15—maintain organisation of stereocilia10,11,12; calcium and potassium entering cell are removed by calcium pump encoded by Pmca213 and potassium channel encoded by KCNQ414 respectively; and otoferlin (encoded by OTOF) may help control neurotransmitter release at synapse15