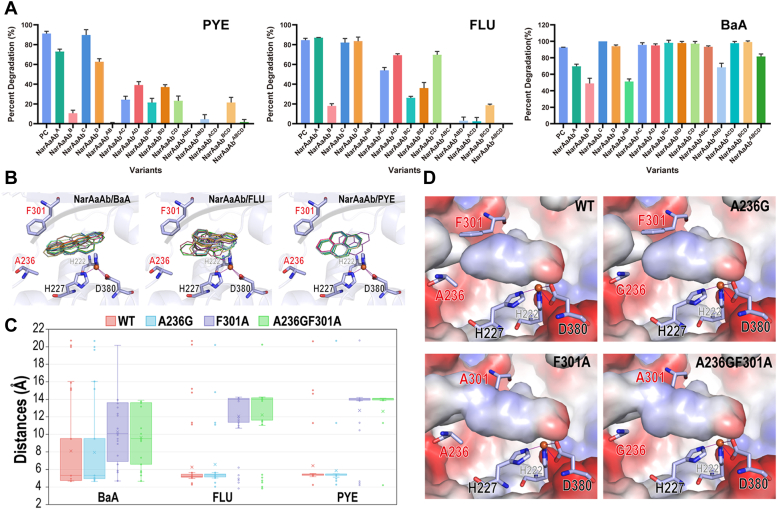
Figure 3.
The degradation of HMW-PAHs by NarAaAb variants and analysis of key residues in NarAa.A, the degradation of PYE, FLU, and BaA by NarAaAb variants. PYE: pyrene; FLU: fluoranthene; BaA: benzo[a]anthracene. PC: E. coli BL21(DE3) containing pET28a-narAaAb and pACYCDuet-phdCD without mutations; NarAaAbA: NarAaAbA236G; NarAaAbB: NarAaAbF301A; NarAaAbC: NarAaAbI317A; NarAaAbD: NarAaAbF376A; NarAaAbAB: NarAaAbA236G-F301A; NarAaAbAC: NarAaAbA236G-I317A; NarAaAbAD: NarAaAbA236G-F376A; NarAaAbBC: NarAaAbF301A-I317A; NarAaAbBD: NarAaAbF301A-F376A; NarAaAbAD: NarAaAbA236G-F376A; NarAaAbABC: NarAaAbA236G-F301A-I317A; NarAaAbABD: NarAaAbA236G-F301A-F376A; NarAaAbACD: NarAaAbA236G-I317A-F376A; NarAaAbBCD: NarAaAbF301A-I317A-F376A; NarAaAbABCD: NarAaAbA236G-F301A-I317A-F376A. B, the docking results of WT of NarAa with three representative substrates. Multiple docking runs of the substrate are depicted by thin sticks, while residues of the mutation sites 236 and 301, as well as the iron coordination residues, are displayed with regular sticks. C, a box plot illustrating the distances between the center-of-mass of docked substrates and the iron atom. Molecular docking was performed with 100 sampling runs. D, the electrostatic potential surface of different variants of NarAa, depicted without substrates, with negative potential in red and positive potential in blue.