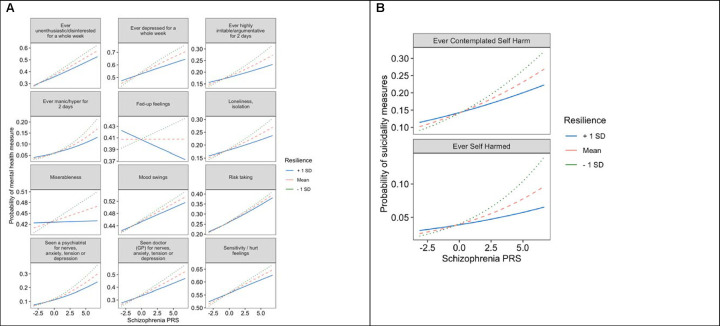
Figure 4.
Resilience scores moderate the penetrance of schizophrenia risk scores, enhancing self-reported mental well-being and reducing self-harm behaviors. A graphical representation of statistically interactive effects of schizophrenia (SCZ) risk and resilience scores on self-reported indicators of mental health provided by UK Biobank participants at the time of enrollment. All measures included in our analysis were scored as binary (yes/no) events. The results shown in this plot for resilience scores correspond to the scores calculated using resilience-associated SNPs that exhibit minimal linkage disequilibrium with mild-risk SNPs for SCZ (R2 value of 0.2 or less). (A) Line plots depicting the significant interaction effects of resilience scores and SCZ risk scores on self-reported mental health measures. The x-axes represent the standardized SCZ risk scores. The y-axis shows the fitted probability values of self-reported mental health measures for which resilience and SCZ risk scores exhibited a significant interaction effect. The lines in the plot depict the effects of SCZ risk at different levels of resilience. The solid blue line denotes the effect of SCZ risk among individuals with a resilience score one standard deviation above the sample mean. The dashed light-red line denotes the effect of SCZ risk at a mean level of resilience. The dotted green line denotes the effect of SCZ risk among individuals with a resilience score one standard deviation below the sample mean. (B) Line plots depicting the significant interactions of resilience and SCZ risk scores on probability of self-reported suicidality measures. The y-axes show the probabilities of both lifetime engagement in self-harm and ideation of self-harm among UK Biobank participants. The x-axes represent the standardized SCZ risk scores. Each line represents the effect of SCZ risk scores on likelihood of participants any suicidality based on levels of resilience. The solid blue line depicts the effect of SCZ risk scores among individuals with resilience one standard deviation above the sample mean. The dashed light-red line depicts the effect of SCZ risk scores at mean levels of resilience. The dotted green line depicts the effect of SCZ risk scores among individuals with resilience scores one standard deviation below the sample mean. We note that y-axes for all plots were scaled according to each outcome variable to enhance visualization of the interaction effects.