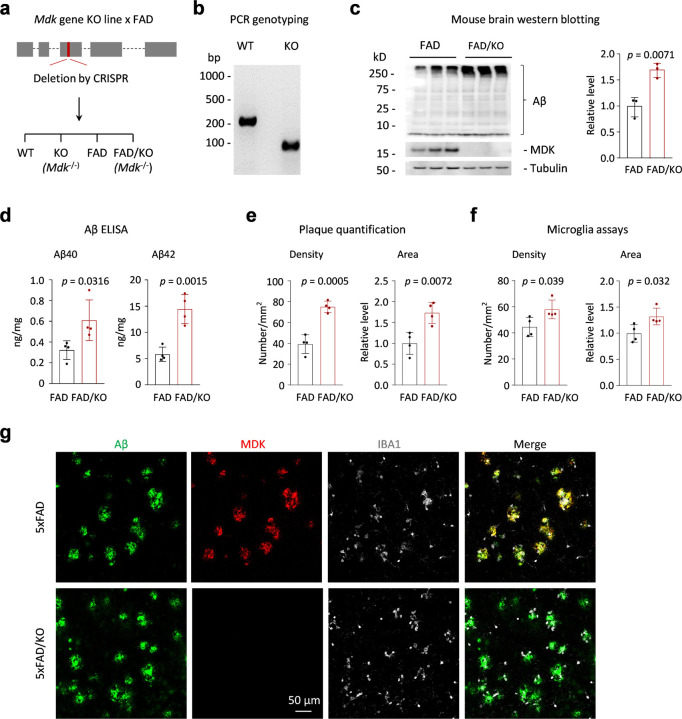
Figure 3. Mdk gene knockout in FAD results in Aβ accumulation, plaque increase and microglia activation.
a, The diagram of the Mdk gene structure, which comprises five exons, including the first exon as the 5’ untranslated region. We targeted a CRISPR-mediated deletion of a specific DNA segment within exon 3, resulting in a gene knockout that disrupts the open reading frame sequence. Crossbreeding of the Mdk KO with FAD resulted in the generation of four genotypes for comparisons. b, PCR genotyping of the WT and homogenous Mdk KO. c, Western blotting to confirm the loss of MDK protein and the increase of Aβ in the brain of heterogenous FAD mice with homogenous Mdk KO (12-month-old, n = 3 replicates). d, Aβ ELISA analysis (n = 4 replicates). e, Quantification of amyloid plaque density and area (n = 4 replicates). f. Quantification of microglia density and area (n = 4 replicates). g. Co-immunofluorescence staining of Aβ, MDK and IBA1 in the mouse brains. Scale bar, 50 µm. Statistical significance is analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test.