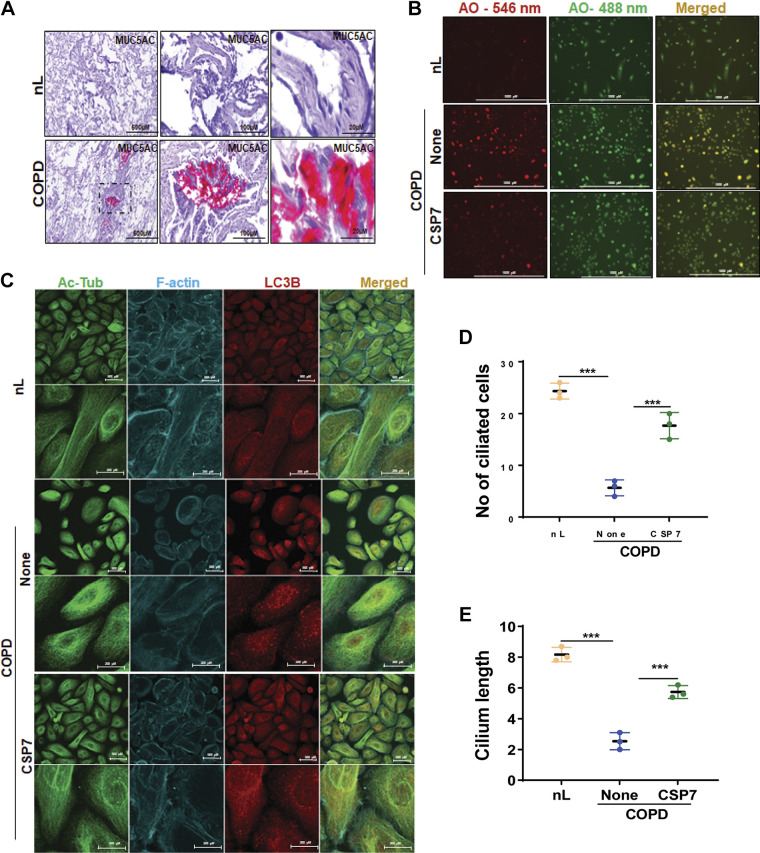
Figure 2.
CSP7 alleviates MH and cilia shortening in AECs from COPD lungs. A: IHC images showing increased MUC5AC staining in the lung sections of patients with COPD (scale bar 500 µM, 100 µM, and 20 µM). B: acridine orange (AO) staining of AECs from nL and COPD. AECs from COPD lungs were left untreated or treated with CSP7 in vitro for 6 h, stained with acridine orange (acidic vesicles), and subjected to fluorescence microscopy (scale bar 1,000 µm). C: immunofluorescence staining and colocalization of Ac-Tub/LC3B in AECs of nL, and COPD lungs treated as in Fig. 1D (scale bar 500 µM and 200 µM). Image represents the findings of two independent experiments. Bar graph showing the number of ciliated cells (D) and cilia length (E) in AECs from nL, and COPD lungs treated with or without CSP7 or CP. Each experiment was repeated at least two to three times, and data are presented as means + SD, and ***P < 0.001 were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test and log-rank tests, respectively. Ac-Tub, acetylated tubulin; AECs, airway epithelial cells; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CSP7, caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide; MH, mucus hypersecretion; MUCAC, mucin 5AC; nL, “normal” lung; AO, acridine orange.