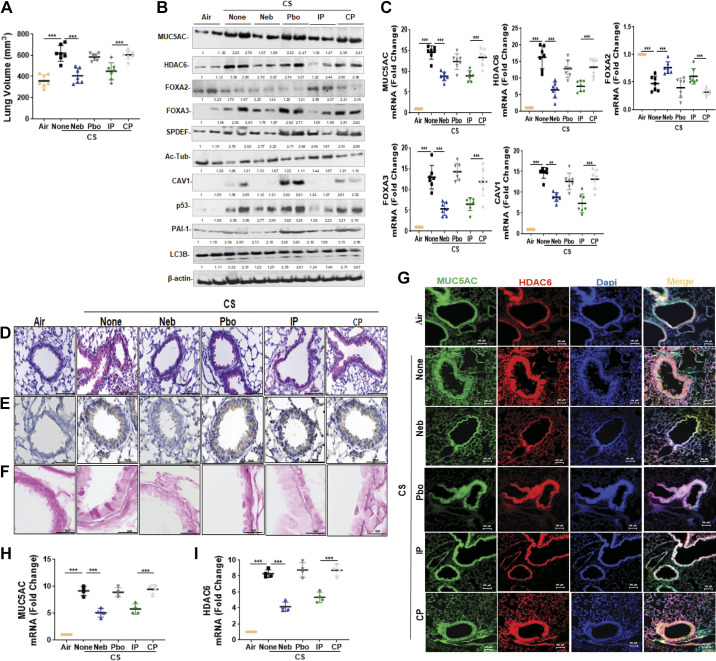
Figure 4.
CSP7 mitigates CS-LI in WT mice. WT mice (n = 10/group) were kept in ambient Air or exposed to CS for 4 h/day 5 days a week as described in materials and methods. After 16 wk, WT mice exposed to CS were left untreated (None) or treated with CSP7 (5.8 mg) in 30 mL of PBS containing lactose monohydrate (154 mg) or placebo (Pbo) alone 2 h/day 5 days a week for 4 wk using a nebulization tower, or by IP injection of 1.5 mg/kg of CSP7 or CP/day 5 days a week for 4 wk. A: all mice were subjected to lung volume measurements 20 wk after CS exposure. Total lung homogenates were analyzed for MCM, autophagy marker, and β-actin proteins (B) and their mRNAs (C). Lung sections of above mice were subjected to IHC staining for MUC5AC (D) and HDAC6 (E) (scale bar 100 µM). F: lung sections were subjected Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining to visualize goblet cells and scale bar 20 µM. G: immunofluorescence staining for MUC5AC and HDAC6 colocalization (scale bar 100 µM). Total RNA from tracheal epithelial cells isolated from mice (n = 4) treated as in A and was analyzed for MUC5AC (H) and HDAC6 (I) mRNA by qPCR. Experiments were performed at least two times, and data are presented as means + SD and **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test and log-rank tests, respectively. CSE, cigarette smoke extract; CSP7, caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide; HDAC6, histone deacetylase 6; MUC5AC, mucin 5AC; WT, wild type.