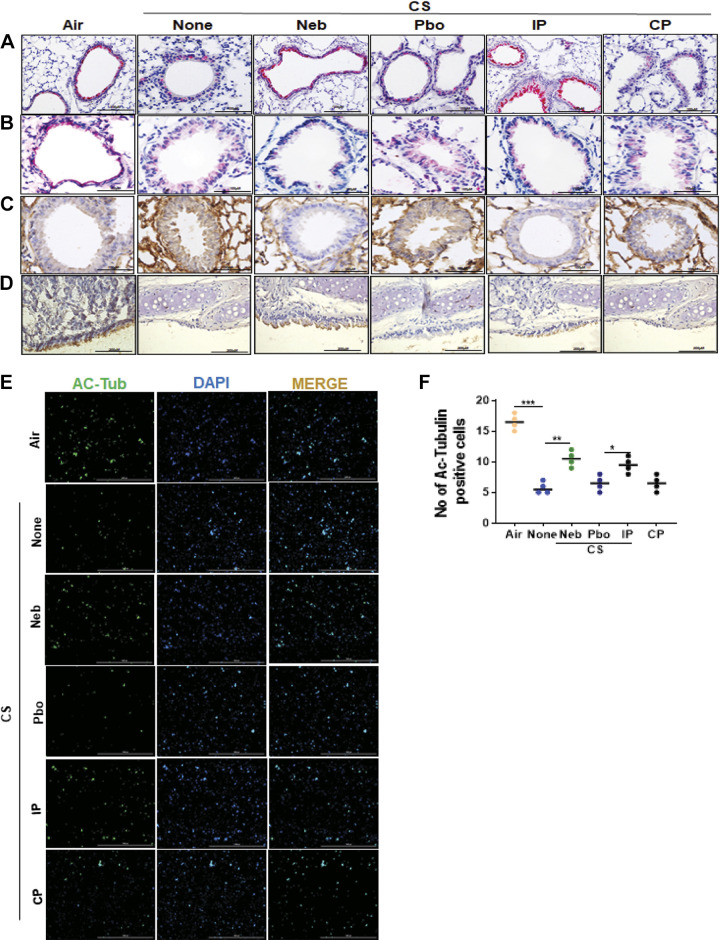
Figure 5.
CSP7 treatment attenuates airway epithelial injury in WT mice with CS-LI. IHC images (scale bar 100 µM) showing the expression of acetylated α-tubulin (cilia) (A) and LC3B (B) in lung sections of WT mice kept in ambient Air or exposed CS (CSE) for 20 wk with or without CSP7 (Neb and IP) treatment. C: IHC staining (scale bar 100 µM) for CAV1 in lung sections of CSE WT mice left untreated or treated with CSP7 (Neb) or placebo (Pbo) via airways by nebulization or treated with CSP7 or CP by intraperitoneal injection. Ambient air kept mice were used as controls. D: IHC analyses of lung trachea sections showed decrease in acetylated α-tubulin staining in CSE WT mice, which is reversed by CSP7 treatment (scale bar 200 µM). E: immunofluorescence imaging for acetylated α-tubulin (Ac-Tub) for cilia in TECs isolated from CSE WT mice treated as in A (scale bar 1,000 µm). F: graph showing number of Ac-Tub-positive cells. Experiments were repeated at least two times, and data are presented as means + SD and *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test and log-rank tests, respectively. CAV1, caveolin‐1; CSE, cigarette smoke extract; CSP7, caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide; WT, wild type.