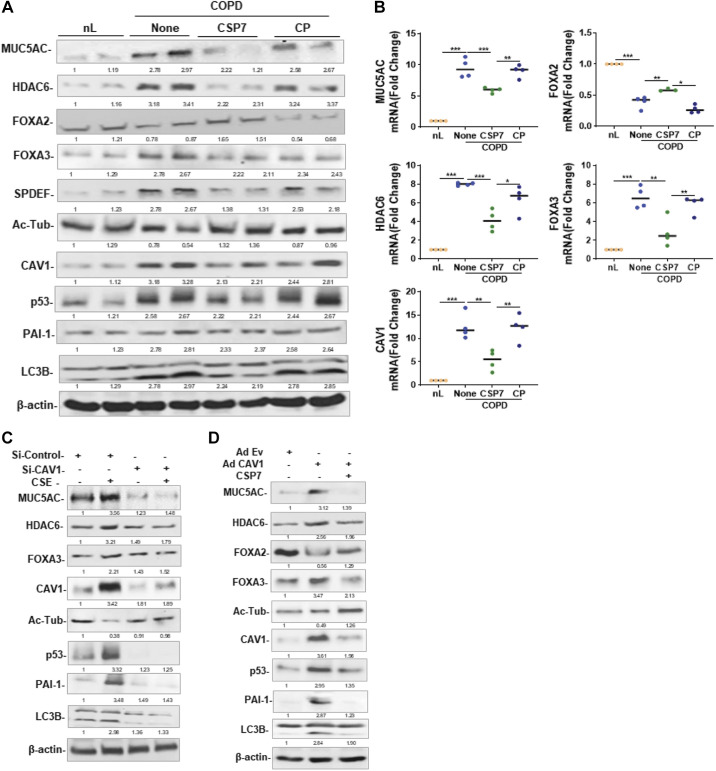
Figure 7.
Effects of CSP7 on MUC5AC and MCC markers in human COPD tissues and AECs ex vivo. Human nL (n = 4) tissues from control donors and COPD lung (n = 4) tissues were left untreated or treated with 10 µM CSP7 or CP in dishes for 72 h. A: Western blotting of COPD lung tissues homogenates for MUC5AC, HDAC6, FOXA2, FOXA3, SPDEF, acetylated tubulin (Ac-Tub), CAV1, p53, PAI-1, LC3BII, and β-actin proteins. B: total RNA from nL and COPD tissues treated as in A was analyzed for MUC5AC, HDAC6, FOXA2, FOXA3, and CAV1 mRNAs by qPCR. C: AECs isolated from nL tissues were treated with control siRNA (siControl) or CAV1 siRNA (siCAV1), and cells were left untreated or treated with CSE. The lysates were immunoblotted for MUC5AC, HDAC6, FOXA3, Ac-Tub, CAV1, p53, PAI-1 LC3BII, and β-actin. D: AECs isolated from nL were transduced with Ad-Ev or Ad-Cav1. These cells were later treated with or without CSP7, and the lysates were tested for MUC5AC and other listed proteins by Western blotting. Experiment was repeated at least two times, and data are presented as means + SD and *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test and log-rank tests, respectively. AECs, airway epithelial cells; CAV1, caveolin‐1; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CSE, cigarette smoke extract; CSP7, caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide; FOXA2, forkhead box protein A2; HDAC6, histone deacetylase 6; MUCAC, mucin 5AC; nL, “normal” lung; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; SPDEF, domain-containing E26 transformation-specific like factor.