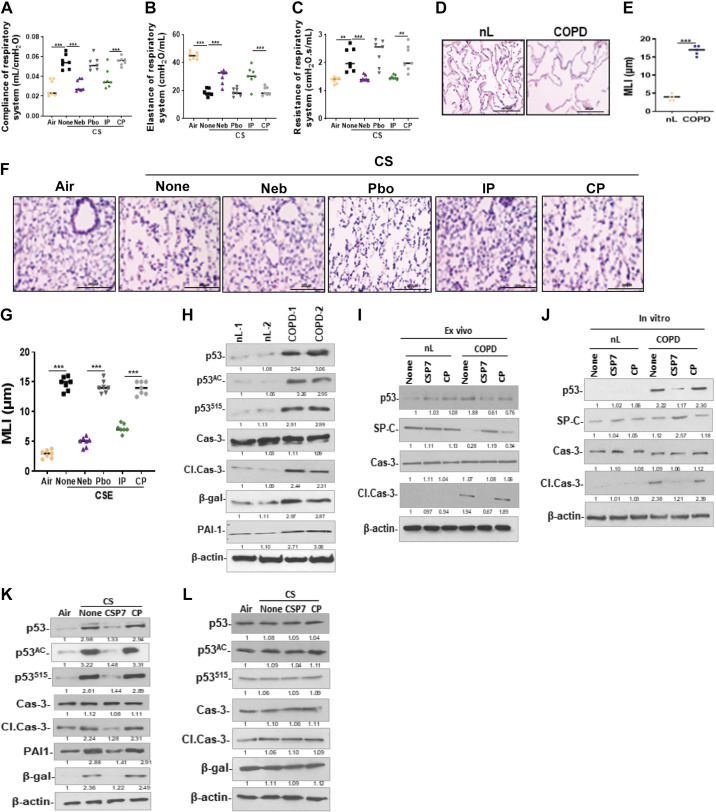
Figure 10.
CSP7 inhibits p53 and improves viability in AT2 cells from mice with CS-LI and in human COPD lung tissues. WT mice (n = 10/group) were exposed to CS for 4 h/day 5 days a week. After 16 wk, CS-exposed (CS) WT mice were left untreated (None) or treated via airways to formulated CSP7 (Neb) or placebo (Pbo) alone 2 h daily 5 days a week for 4 wk using a nebulization tower. WT mice with CS-LI and IP injected CSP7 or CP daily 5 days a week for 4 wk were used as controls for comparison. Compliance of respiratory system (Crs; A), elastance of respiratory system (Ers; B), and resistance of respiratory system (Rrs; C). microscopic images of H&E-stained sections (scale bar 200 µM; D) and bar graph showing increased MLI in COPD lung than nL (E). Microscopic images of H&E-stained lung sections (scale bar 200 µM; F) and bar graph showing MLI in mice with CS-LI vs those kept in ambient AIR (G). H: AT2 cells isolated from nL and COPD lung tissues were analyzed for p53, PAI-1, senescence (β-Gal), apoptosis (Cl. Cas-3), and β-actin by Western blotting. I: AT2 cells isolated from human control (nL) and COPD lung tissues left untreated (None) or treated with CSP7 or CP for 72 h ex vivo were immunoblotted for p53, SP-C, Cl. Cas-3, Cas-3, and β-actin. J: lysates of AT2 cells isolated from nL and COPD lung tissues treated in vitro were immunoblotted for p53, SP-C, apoptosis, and β-actin. AT2 isolated from ambient AIR kept, or CS WT (K) or PAI-1-deficient (L) mice left untreated or treated with CSP7 or CP by IP injection were analyzed for above proteins by Western blotting. Each experiment was repeated at least two times, and data are presented as means + SD, and **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test and log-rank tests, respectively. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CSE, cigarette smoke extract; CSP7, caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide; HDAC6, histone deacetylase 6; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; WT, wild type.