Figure 1. Novel TIE:EGFP zebrafish enhancer reporter is expressed in advanced melanomas.
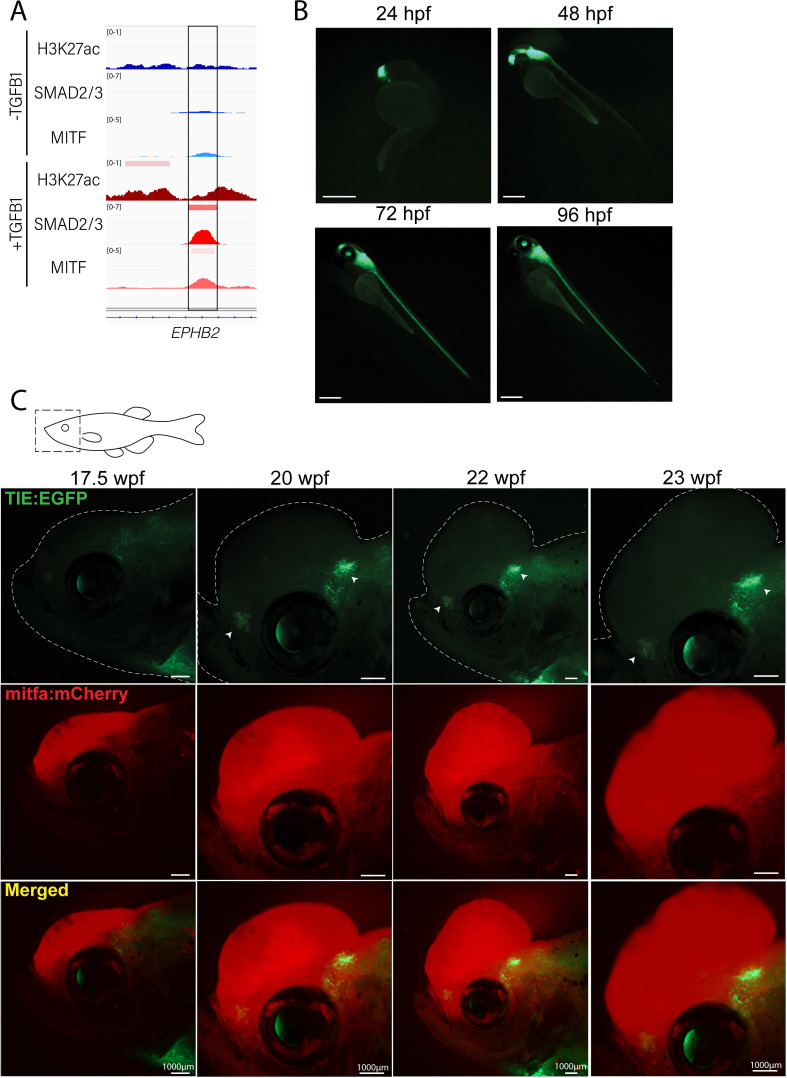
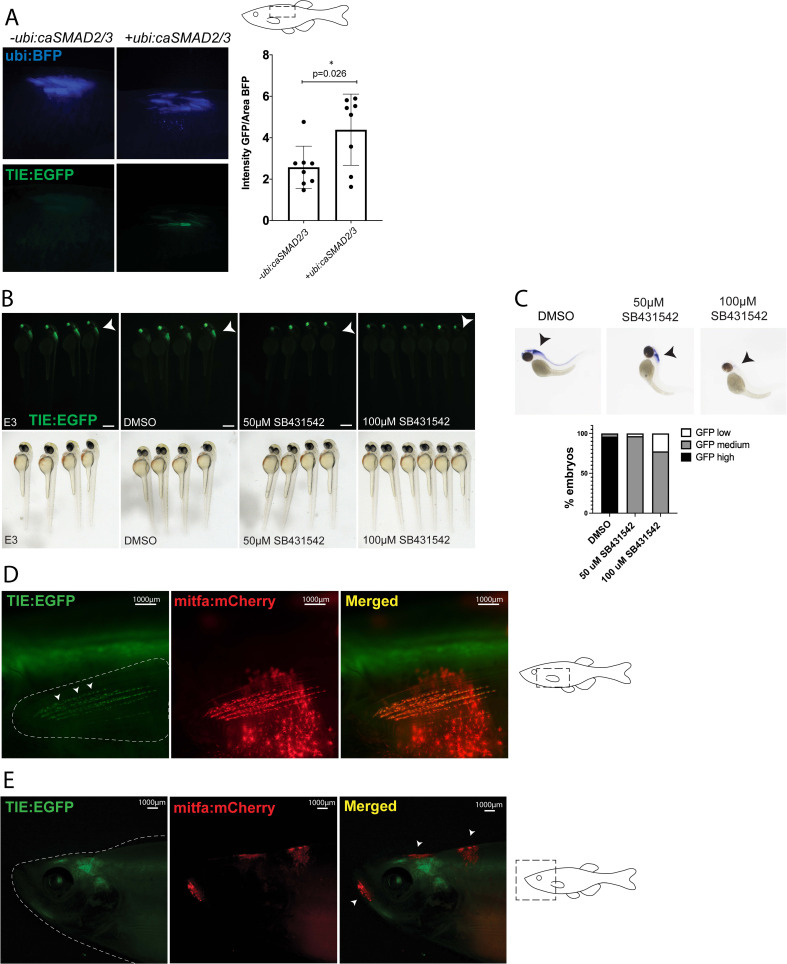
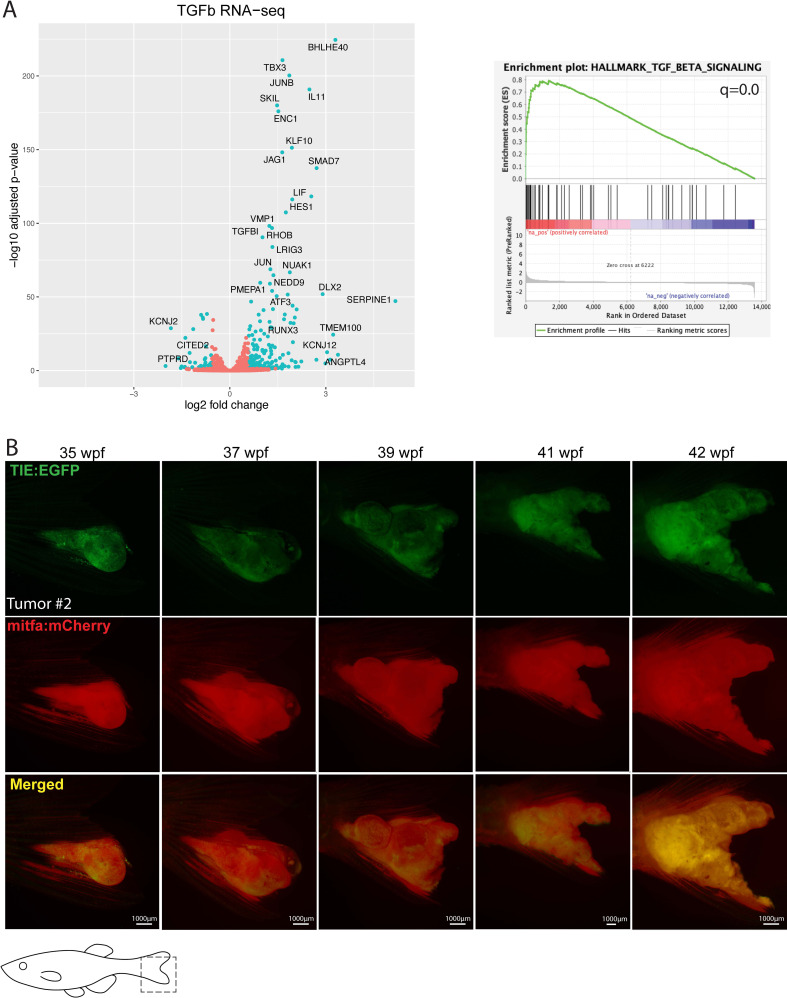
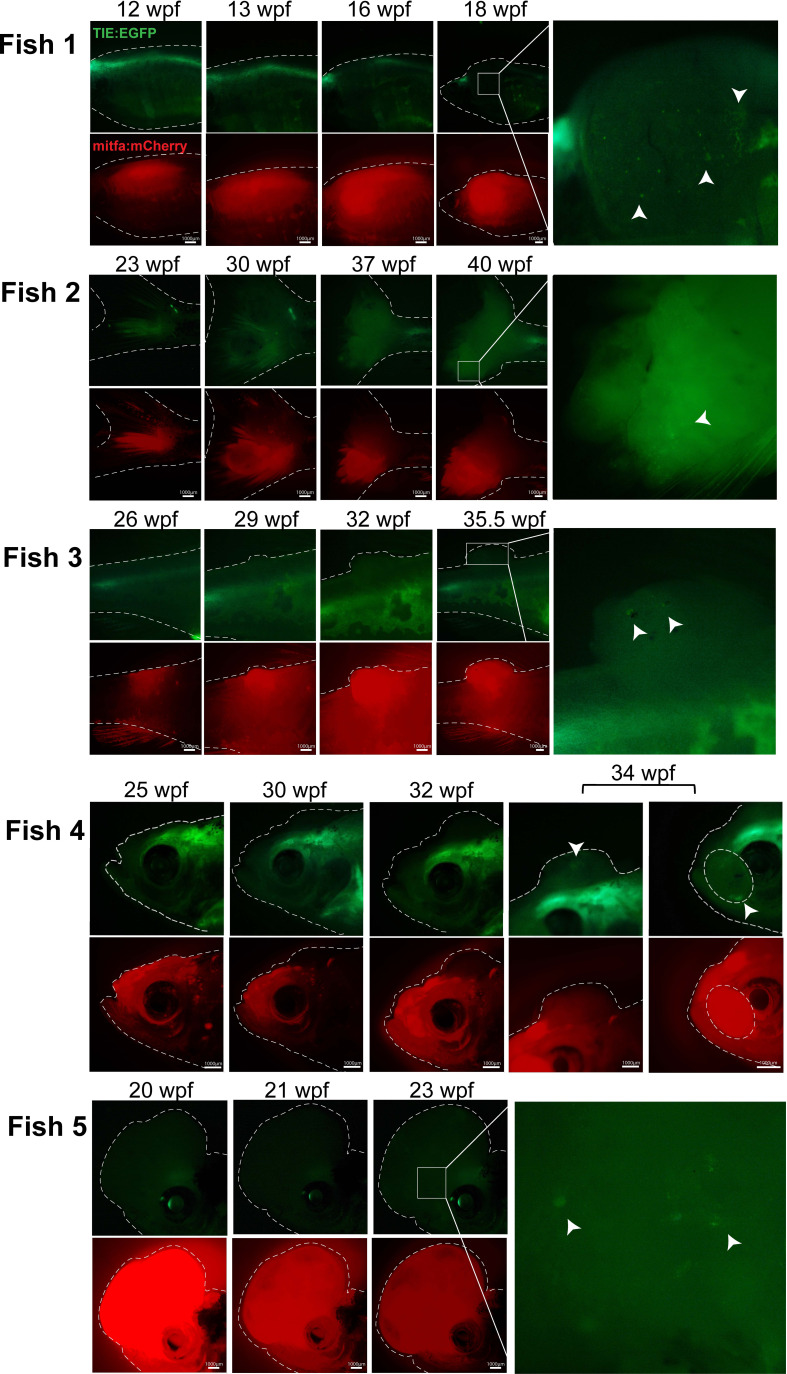
(A) TGFb-induced enhancer (TIE) used to construct TIE:EGFP reporter determined by H3K27ac, SMAD2/3, and MITF ChIP-seq peaks in A375s+/-TGFB1. There is unique H3K27ac and SMAD2/3 binding upon stimulus. (B) TIE:EGFP expression throughout zebrafish development. Scale bars represent 500 µm. (C) TIE:EGFP expression across melanomagenesis indicated by arrowheads. Representative images shown. Additional tumors shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Illustrated fish diagram in (C) created with BioRender.com, and published using a CC BY-NC-ND license with permission.
© 2024, BioRender Inc
Figure 1 was created using BioRender, and is published under a CC BY-NC-ND license. Further reproductions must adhere to the terms of this license.