FIGURE 4.
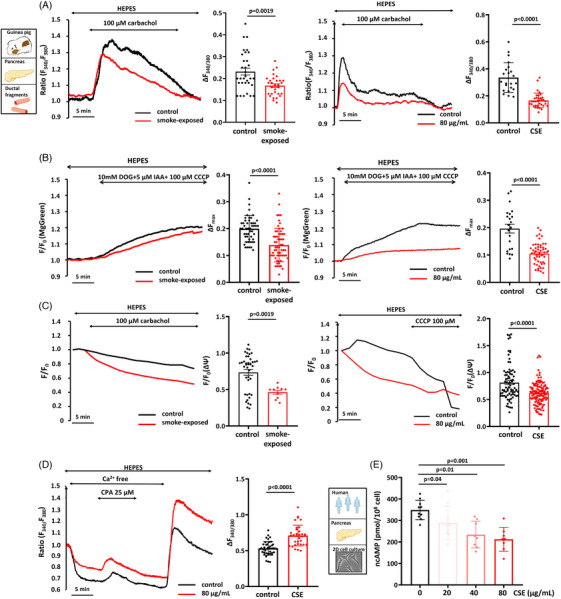
Smoke inhalation and cigarette smoke extract (CSE) reduce the maximum elevation of [Ca2+]i, ATP level and decrease mitochondrial membrane potential in isolated guinea pig pancreatic ductal cells. (A) Representative traces and summary data of the δRatiomax showing the effect of smoking and CSE on [Ca2+]i. The maximum response to 100 µM carbachol was significantly smaller in pancreatic ductal fragments isolated from the smoking animals and also after pretreatment with 80 µg/mL CSE (n = 5−7). (B) Total ATP depletion induced by a combination of deoxyglucose/iodoacetate/carbonyl cyanide 3‐chlorophenylhydrazone showed a significantly lower level of intracellular ATP in pancreatic ductal fragments isolated from the smoking animals or treated with CSE (n = 5−7). (C) Mitochondrial membrane potential was significantly diminished by smoking or CSE incubation (n = 5−7). (D) Representative traces of [Ca2+]i demonstrating that CSE incubation significantly reduced extracellular Ca2+ influx in guinea pig pancreatic ductal fragments. (E) Summary data for cAMP measurements showing that total intracellular cAMP level was significantly reduced after preincubation of 20, 40 and 80 µg/mL CSE in CAPAN‐1 cells (n = 3).
