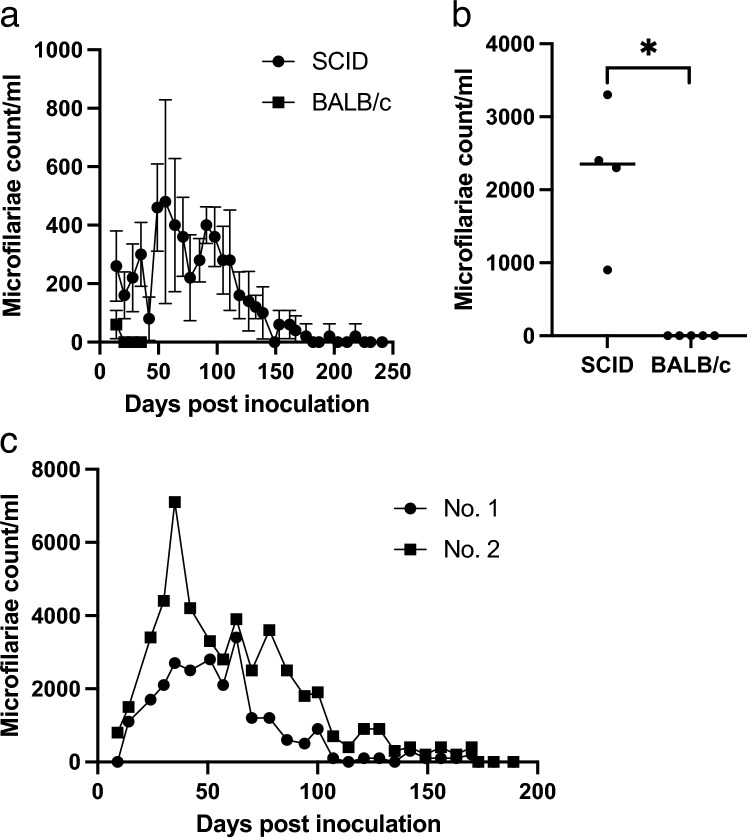
Figure 1.
Long-term D. immitis microfilariaemia in a rodent model using the SCID mouse. (a) Comparison of the peripheral blood microfilaremia period between SCID mice and BALB/c mice. Mice (n = 5) were inoculated with 3.0 × 104 microfilariae via the tail vein, and peripheral blood microfilaremia was monitored every week. SCID mice showed significantly prolonged microfilaremia (Mann–Whitney test, p < 0.01). Error bars = mean ± SD. (b) Microfilaremia count of the blood collected by cardiac puncture of the individual mice. Cardiac puncture was done after peripheral blood microfilariae had disappeared. *p < 0.01 (Mann–Whitney test). (c) High microfilariae dose test. Microfilaremia of the SCID mice inoculated with a high dose (1.9 × 105) of D. immitis microfilariae (n = 2). SCID severe combined immunodeficiency.