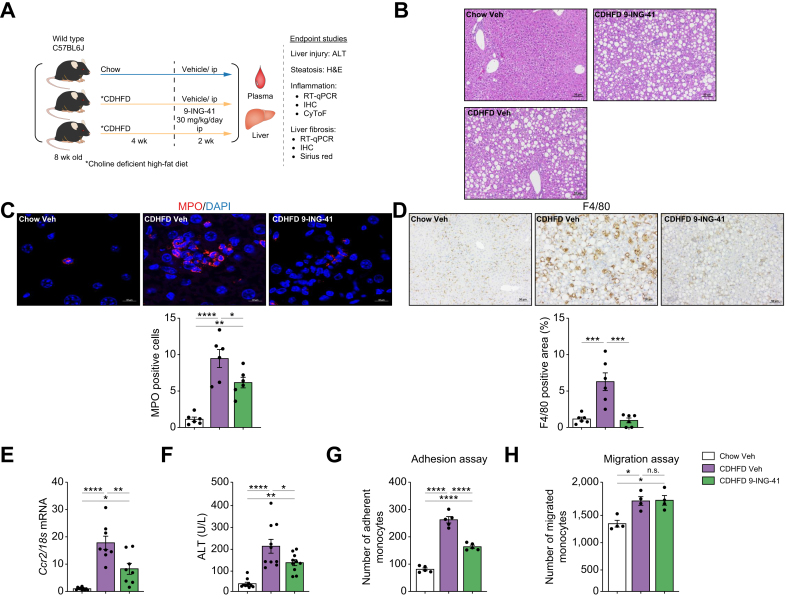
Fig. 6.
Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3 inhibition with elraglusib improves liver injury and inflammation in choline-deficient high-fat diet (CDHFD)-induced murine metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH).
Eight-week-old wild-type (WT) C57BL/6J mice were fed either a chow diet or CDHFD for 6 weeks and treated with either vehicle (Veh) or the GSK3 inhibitor 9-ING-41 (intraperitoneally 30 mg/kg daily for 2 weeks). (A) Schematic of the feeding experiment. (B) Representative images of H&E staining of the liver sections. (C) Myeloperoxidase (MPO) immunofluorescence staining (red) Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Images are shown at a 63 × magnification. (D) F4/80 immunostaining of liver sections (left). F4/80-positive areas were quantified in five random 10 × microscopic fields and averaged for each animal (right). (E) Hepatic mRNA expression levels of Ccr2. (F) Plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (n = 5–10). Quantification of (G) monocytes adherent to liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) (n = 5), (H) and migrating monocytes (n = 3) in the different experimental groups. Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM; ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001, ∗∗∗∗p <0.0001, ns, non-significant (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison). Scale bars: 10 μm (C), 50 μm (B,D).