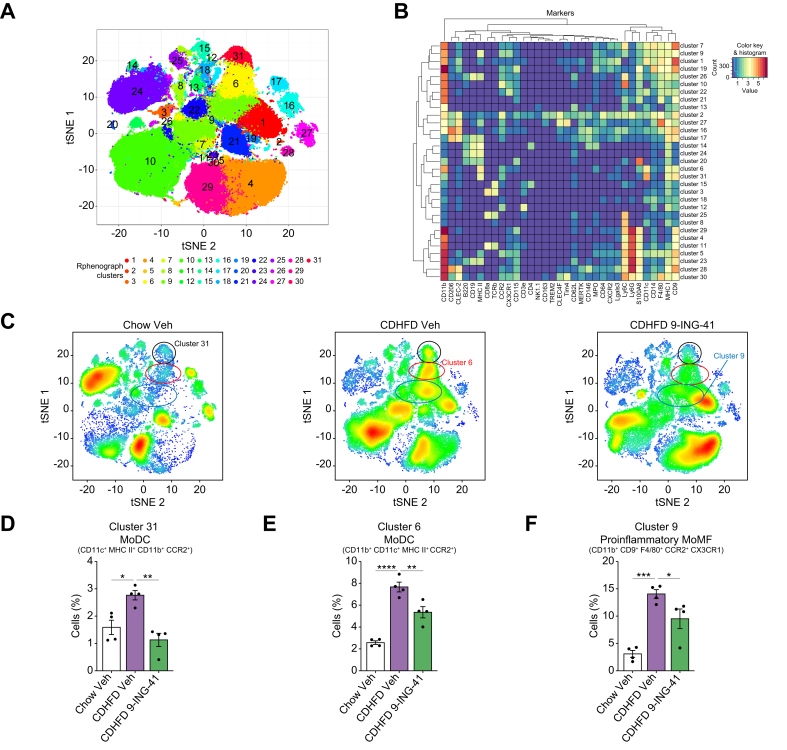
Fig. 7.
Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3 inhibition with elraglusib attenuates the recruitment of proinflammatory myeloid cells in the liver of choline-deficient high-fat diet (CDHFD)-fed mice.
Cytometry by time of flight (CyTOF) was performed on intrahepatic leukocytes (IHLs) of chow-fed mice and CDHFD-fed mice treated with the GSK3 inhibitor elraglusib (9-ING-41). (A) Thirty-one unique clusters were defined by a panel of 32 cell-surface markers, including CD45 and two intracellular markers (myeloperoxidase [MPO] and S100A8) using the Rphenograph clustering algorithm and visualized on a tSNE plot. (B) Heatmap demonstrating the distribution and relative intensity of the markers used in clustering analysis. (C) Representative tSNE plots of each experimental group. Red indicates high-frequency categorization of cells into a cluster, and blue indicates low frequency. Clusters 31 (D) and 6 (E) are consistent with monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs), whereas cluster 9 (F) is consistent with proinflammatory monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMFs). Bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM; ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.001, ∗∗∗∗p <0.0001 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison; n = 4). tSNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.